School vaccination exemptions in U.S. now highest on record among kindergartners, CDC reports
By Sara Moniuszko
9 November 2023
(CBS News) – A record number of American kindergarten students started school last year with an exemption from one of the key vaccines health authorities require, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In the report published Thursday, the CDC examined immunization program data to assess vaccination coverage and exemption status for four childhood vaccines:
- Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR)
- Diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis vaccine (DTaP)
- Poliovirus (polio) vaccine
- Varicella vaccine (protects against chickenpox)
Among children enrolled in public and private kindergarten during the 2022-23 school year, the report found vaccination coverage remains lower than the pre-pandemic levels, at 93%, down from 95%.
Vaccination exemptions increased to 3% of kindergarten students — the highest exemption rate ever reported in the country — and a vast majority of those exemptions were not for medical reasons.
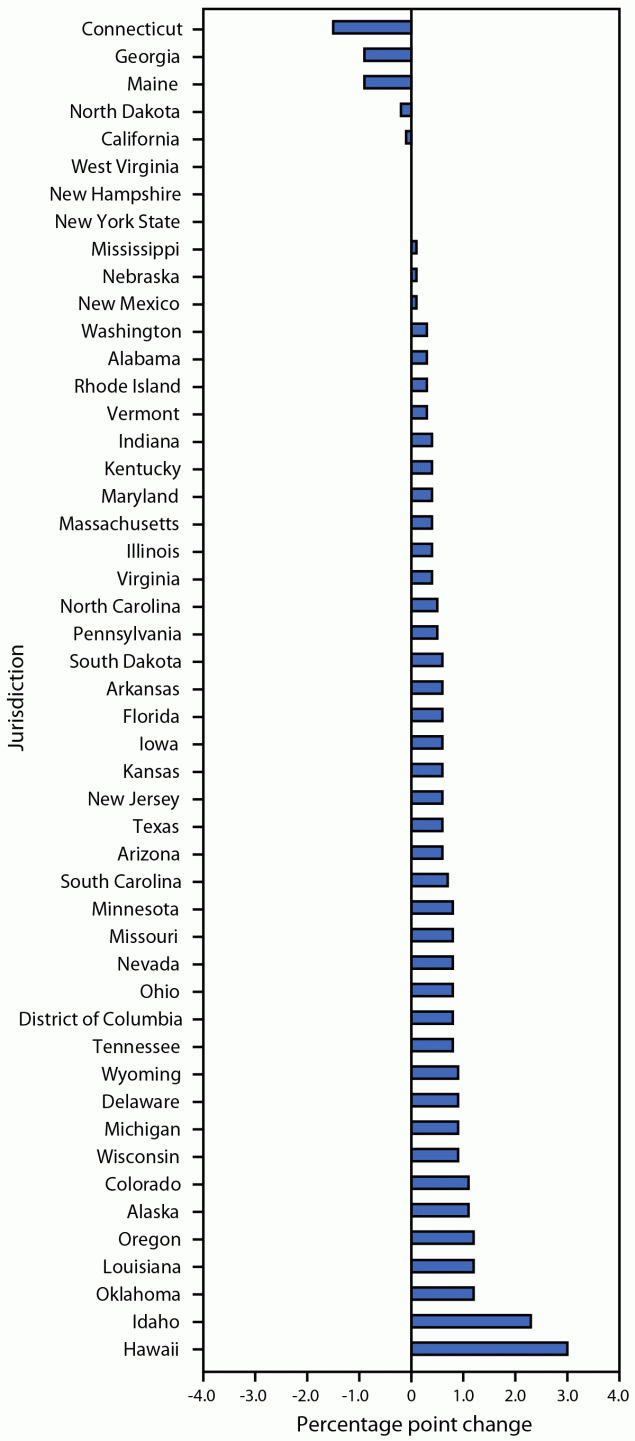
“Overall, 3.0% of kindergartners had an exemption (0.2% medical and 2.8% nonmedical) from one or more required vaccines,” the report noted. “Nonmedical exemptions account for (greater than) 90% of reported exemptions, and approximately 100% of the increase in the national exemption rate.”
A medical exemption is allowed when a child has “a medical condition that prevents them from receiving a vaccine,” according to the CDC. Nonmedical exemptions, for religious or philosophical reasons, are allowed in all but three states, the agency says. In recent years, New York and California have passed laws clamping down on nonmedical exemptions after outbreaks of measles.
While the new report did not determine whether the uptick in nonmedical exemptions reflects an increase in opposition to vaccination or if parents are skipping the shots due to barriers or inconvenience, it does come at a time when vaccine hesitancy remains high, a sentiment amplified by anti-vaccine activists during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The CDC stresses the importance of making sure children are fully vaccinated against common and sometimes serious infectious diseases before entering school, since clusters of undervaccinated kids can lead to outbreaks.
School vaccination exemptions now highest on record among kindergartners, CDC reports
Coverage with Selected Vaccines and Exemption from School Vaccine Requirements Among Children in Kindergarten — United States, 2022–23 School Year
ABSTRACT: U.S. states and local jurisdictions set vaccination requirements for school attendance and conditions and procedures for exemptions from these requirements. States annually report data to CDC on the number of children in kindergarten who meet, are exempt from, or are in the process of meeting requirements. National- and state-level estimates for complete vaccination with measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR); diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis vaccine (DTaP); poliovirus vaccine (polio); and varicella vaccine (VAR); exemptions from vaccination; and legally allowed kindergarten attendance while meeting requirements were based on data reported by 49 states and the District of Columbia (DC) for the 2022–23 school year. This kindergarten class became age-eligible to complete most state-required vaccinations during the COVID-19 pandemic. National coverage remained near 93% for all vaccines; exemptions were low but increased to 3%, compared with those during the 2021–22 school year (2.6%). At the state level, coverage with MMR, DTaP, polio, and VAR decreased in 29, 31, 28, and 25 states, respectively, compared with coverage during the 2021–22 school year. Exemptions increased in 40 states and DC, with 10 states reporting an exemption from at least one vaccine for >5% of kindergartners. Schools and providers should work to ensure that students are vaccinated before school entry, such as during the enrollment process, which is often several months before school starts. State and local provisional enrollment periods that allow students to attend school while on a catch-up schedule also provide the opportunity to fully vaccinate students and to prevent nonmedical exemptions resulting from lingering undervaccination due to COVID-19 pandemic–related barriers to vaccination, such as reduced access to vaccination appointments.