Researchers uncover the surprising cause of the Little Ice Age – “We may be underestimating future ice loss from the Greenland ice sheet”
AMHERST, Massachusetts, 15 December 2021 (University of Massachusetts Amherst) – New research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst provides a novel answer to one of the persistent questions in historical climatology, environmental history and the earth sciences: what caused the Little Ice Age? The answer, we now know, is a paradox: warming.
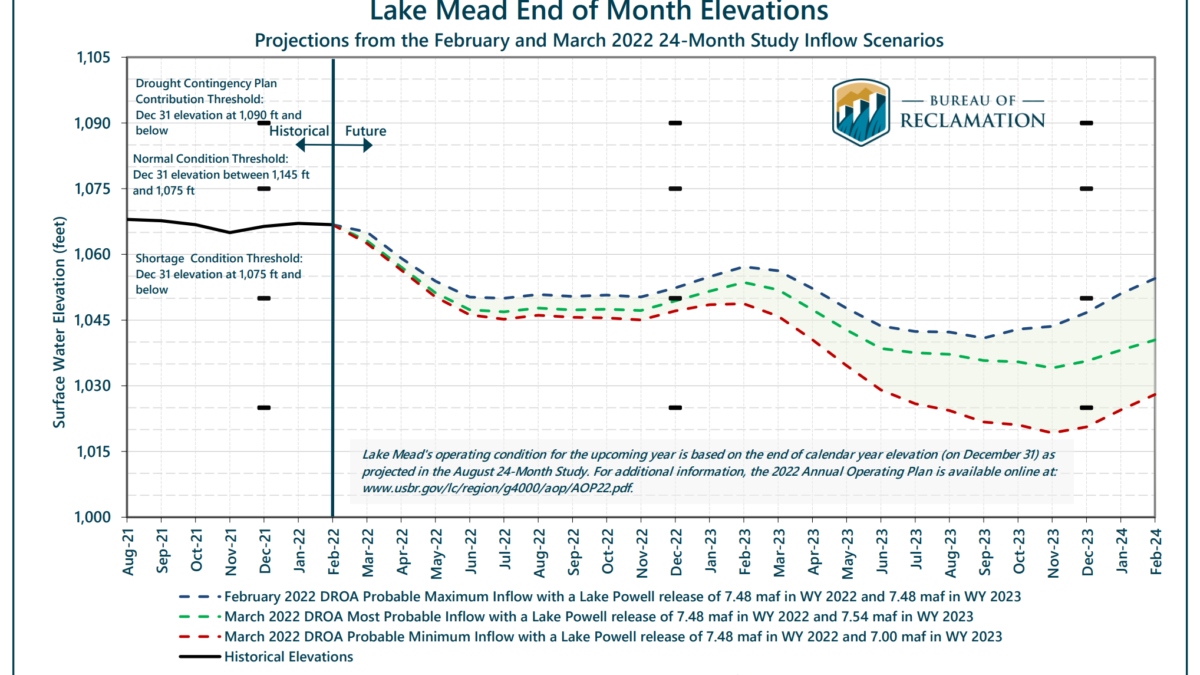
The Little Ice Age was one of the coldest periods of the past 10,000 years, a period of cooling that was particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. This cold spell, whose precise timeline scholars debate, but which seems to have set in around 600 years ago, was responsible for crop failures, famines and pandemics throughout Europe, resulting in misery and death for millions. To date, the mechanisms that led to this harsh climate state have remained inconclusive. However, a new paper published recently in Science Advances gives an up-to-date picture of the events that brought about the Little Ice Age. Surprisingly, the cooling appears to have been triggered by an unusually warm episode.
When lead author Francois Lapointe, postdoctoral researcher and lecturer in geosciences at UMass Amherst and Raymond Bradley, distinguished professor in geosciences at UMass Amherst began carefully examining their 3,000-year reconstruction of North Atlantic sea surface temperatures, results of which were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in 2020, they noticed something surprising: a sudden change from very warm conditions in the late 1300s to unprecedented cold conditions in the early 1400s, only 20 years later.
Using many detailed marine records, Lapointe and Bradley discovered that there was an abnormally strong northward transfer of warm water in the late 1300s which peaked around 1380. As a result, the waters south of Greenland and the Nordic Seas became much warmer than usual. “No one has recognized this before,” notes Lapointe.
Normally, there is always a transfer of warm water from the tropics to the arctic. It’s a well-known process called the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), which is like a planetary conveyor belt. Typically, warm water from the tropics flows north along the coast of Northern Europe, and when it reaches higher latitudes and meets colder arctic waters, it loses heat and becomes denser, causing the water to sink at the bottom of the ocean. This deep-water formation then flows south along the coast of North America and continues on to circulate around the world.
But in the late 1300s, AMOC strengthened significantly, which meant that far more warm water than usual was moving north, which in turn cause rapid arctic ice loss. Over the course of a few decades in the late 1300s and 1400s, vast amounts of ice were flushed out into the North Atlantic, which not only cooled the North Atlantic waters, but also diluted their saltiness, ultimately causing AMOC to collapse. It is this collapse that then triggered a substantial cooling.
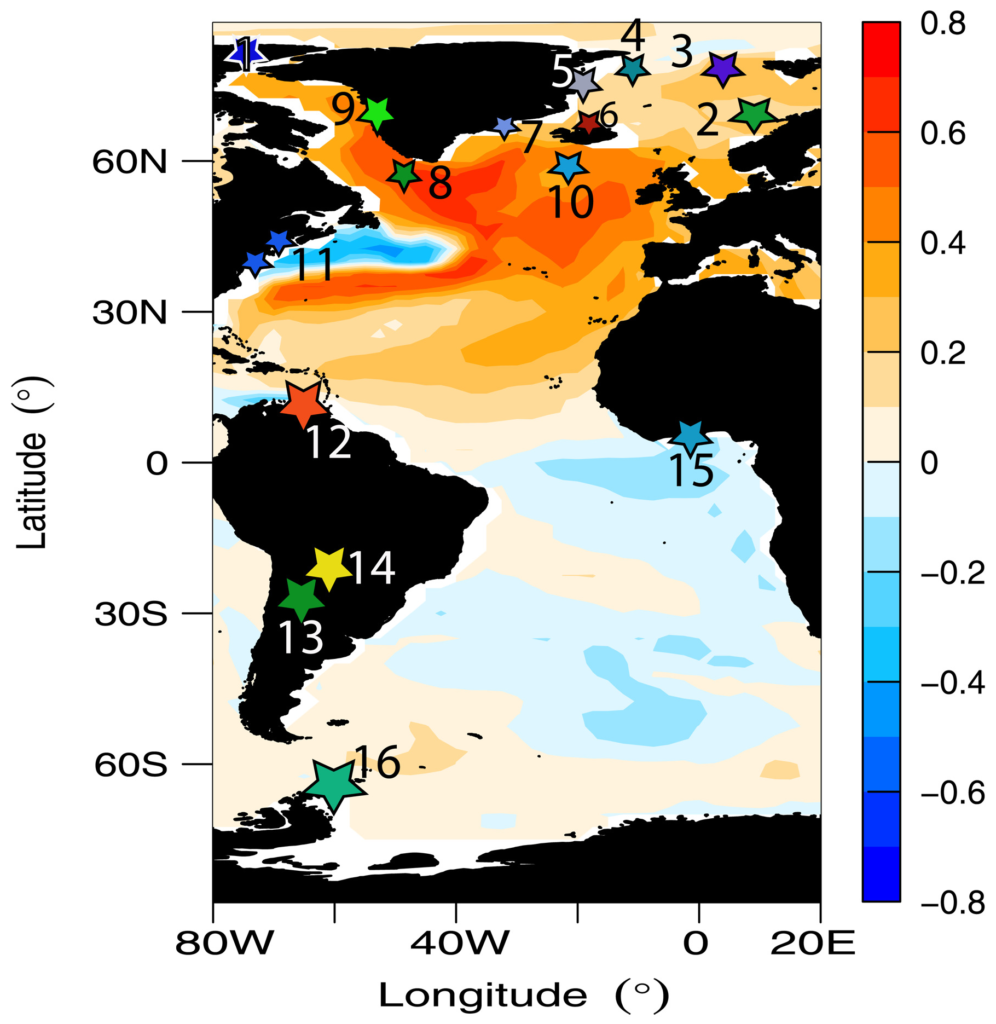
![Upstream and downstream path of the North Atlantic Current in the Arctic. (A) Reconstructed August temperature in the Vøring Plateau (25), compared to AMV. (B) High-resolution IRD on the Eastern Fram Strait [core MSM5/5-712 (28)]. The IRD data were detrended to remove the neoglacial cooling trend. (C) C. neoteretis, a proxy for warm Atlantic waters in Western Fram Strait (core PS93/025) (29). (D) N. labradorica, a proxy for chilled Atlantic waters from core PS2641-4 (30) and IRD reported in Denmark Strait (32). The AMV is filtered by a 21-year Gaussian filter, and the gray-shaded area is the 95 percent confidence level of the reconstruction (23). Graphic: Lapointe and Bradley, 2021 / Science Advances](https://desdemonadespair.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Upstream-and-downstream-path-of-the-North-Atlantic-Current-in-the-Arctic-Lapointe-and-Bradley-2021-Science-Advances-786x1024.png)
Fast-forward to our own time: between the 1950s to the late 1960s, we have also seen a rapid strengthening of AMOC, which has been linked with persistently high pressure in the atmosphere over Greenland. Lapointe and Bradley think the same atmospheric situation occurred just prior to the Little Ice Age—but what could have set off that persistent high-pressure event in the 1380s?
The answer, Lapointe discovered, is to be found in trees. Once the researchers compared their findings to a new record of solar activity revealed by radiocarbon isotopes preserved in tree rings, they discovered that unusually high solar activity was recorded in the late 1300s. Such solar activity tends to lead to high atmospheric pressure over Greenland.
At the same time, fewer volcanic eruptions were happening on earth, which means that there was less ash in the air. A “cleaner” atmosphere meant that the planet was more responsive to changes in solar output. “Hence the effect of high solar activity on the atmospheric circulation in the North-Atlantic was particularly strong,” said Lapointe.
Lapointe and Bradley have been wondering whether such an abrupt cooling event could happen again in our age of global climate change. They note that there is now much less arctic sea ice due to global warming, so an event like that in the early 1400s, involving sea ice transport, is unlikely. “However, we do have to keep an eye on the build-up of freshwater in the Beaufort Sea (north of Alaska) which has increased by 40% in the past two decades. Its export to the subpolar North Atlantic could have a strong impact on oceanic circulation”, said Lapointe. “Also, persistent periods of high pressure over Greenland in summer have been much more frequent over the past decade and are linked with record-breaking ice melt. Climate models do not capture these events reliably and so we may be underestimating future ice loss from the ice sheet, with more freshwater entering the North Atlantic, potentially leading to a weakening or collapse of the AMOC.” The authors conclude that there is an urgent need to address these uncertainties.
This research was supported by funding from the National Science Foundation.
Winter is coming: Researchers uncover the surprising cause of the Little Ice Age
Little Ice Age abruptly triggered by intrusion of Atlantic waters into the Nordic Seas
ABSTRACT: The Little Ice Age (LIA) was one of the coldest periods of the postglacial period in the Northern Hemisphere. Although there is increasing evidence that this time interval was associated with weakening of the subpolar gyre (SPG), the sequence of events that led to its weakened state has yet to be explained. Here, we show that the LIA was preceded by an exceptional intrusion of warm Atlantic water into the Nordic Seas in the late 1300s. The intrusion was a consequence of persistent atmospheric blocking over the North Atlantic, linked to unusually high solar activity. The warmer water led to the breakup of sea ice and calving of tidewater glaciers; weakening of the blocking anomaly in the late 1300s allowed the large volume of ice that had accumulated to be exported into the North Atlantic. This led to a weakening of the SPG, setting the stage for the subsequent LIA.
Little Ice Age abruptly triggered by intrusion of Atlantic waters into the Nordic Seas