Climate collapse could happen fast – “Many scientists knew these things would happen, but we’re taken aback by the severity of the major changes we’re seeing”

By Lois Parshley
20 July 2023
(The Atlantic) – Ever since some of the earliest projections of climate change were made back in the 1970s, they have been remarkably accurate at predicting the rate at which global temperatures would rise. For decades, climate change has proceeded at roughly the expected pace, says David Armstrong McKay, a climate scientist at the University of Exeter, in England. Its impacts, however, are accelerating—sometimes far faster than expected.
For a while, the consequences weren’t easily seen. They certainly are today. The Southwest is sweltering under a heat dome. Vermont saw a deluge of rain, its second 100-year storm in roughly a decade. Early July brought the hottest day globally since records began—a milestone surpassed again the following day. “For a long time, we were within the range of normal. And now we’re really not,” Allegra LeGrande, a physical-research scientist at Columbia University, told me. “And it has happened fast enough that people have a memory of it happening.”
In fact, a growing number of climate scientists now believe we may be careening toward so-called tipping points, where incremental steps along the same trajectory could push Earth’s systems into abrupt or irreversible change—leading to transformations that cannot be stopped even if emissions were suddenly halted. “The Earth may have left a ‘safe’ climate state beyond 1°C global warming,” Armstrong McKay and his co-authors concluded in Science last fall. If these thresholds are passed, some of global warming’s effects—like the thaw of permafrost or the loss of the world’s coral reefs—are likely to happen more quickly than expected. On the whole, however, the implications of blowing past these tipping points remain among climate change’s most consequential unknowns: We don’t really know when or how fast things will fall apart.

Some natural systems, if upended, could herald a restructuring of the world. Take the Thwaites Glacier in West Antarctica: It’s about the size of Florida, with a protruding ice shelf that impedes the glacier’s flow into the ocean. Although the ice shelf’s overall melt is slower than originally predicted, warm water is now eating away at it from below, causing deep cracks. At a certain point, that melt may progress enough to become self-sustaining, which would guarantee the glacier’s eventual collapse. How that plays out will help determine how much sea levels will rise—and thus the future of millions of people.
The fate of the Thwaites Glacier could be independent of other tipping points, such as those affecting mountain-glacier loss in South America, or the West African monsoon. But some tipping points will interact, worsening one another’s effects. When melt from Greenland’s glaciers enters the ocean, for example, it alters an important system of currents called the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. The AMOC is like a conveyor belt, drawing warm water from the tropics north. The water’s salinity increases as it evaporates, which, among other factors, makes it sink and return south along the ocean floor. As more glacial fresh water enters the system, that conveyor belt will weaken. Right now, it’s the feeblest it’s been in more than 1,000 years.
A shutdown of that ocean current could dramatically alter phenomena as varied as global weather patterns and crop yields. Messing with complex systems is chilling precisely because there are so many levers: If the temperature of the sea surface changes, precipitation over the Amazon might too, contributing to its deforestation, which in turn has been linked to snowfall on the Tibetan plateau. We may not even realize when we start passing points of no return—or if we already have. “It’s kind of like stepping into a minefield,” Armstrong McKay said. “We don’t want to find out where these things are by triggering them.”
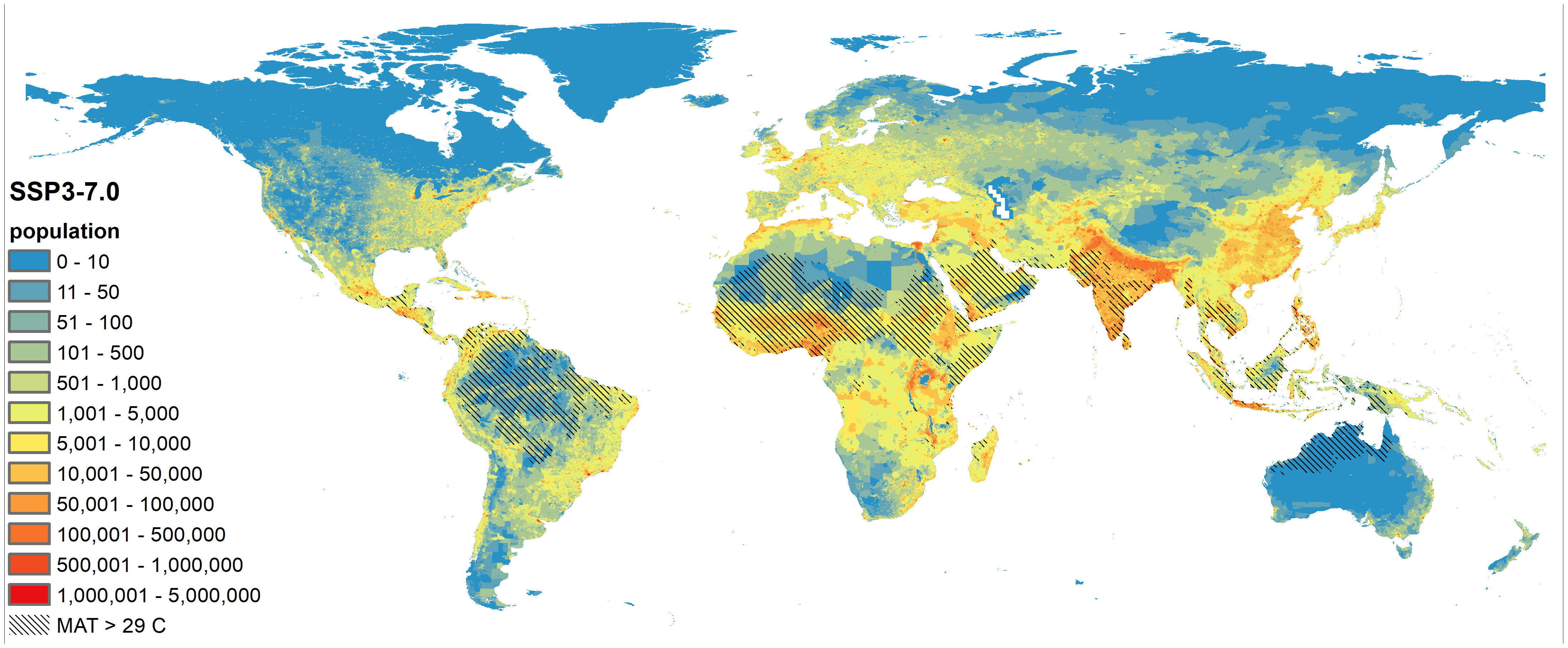
One grim paper that came out last year, titled “Climate End Game,” mapped out some of the potential catastrophes that could follow a “tipping cascade,” and considered the possibility that “a sudden shift in climate could trigger systems failures that unravel societies across the globe.” Chris Field, the director of the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment and a contributor to several IPCC reports, warned that “at some point, the impacts of the climate crisis may become so severe that we lose the ability to work together to deliver solutions.”

James Hansen, one of the early voices on climate, says that measures to mitigate the crisis may now, ironically, be contributing to it. He published a working paper this spring suggesting that a reduction in sulfate aerosol particles—or the air pollution associated with burning coal and the global shipping industry—has contributed to warmer temperatures. That’s because these particles cause water droplets to multiply, which brightens clouds and reflects solar heat away from the planet’s surface. Though the paper has not been peer-reviewed, Hansen predicts that environmentally minded policies to reduce these pollutants will likely cause temperatures to rise by 2 degrees Celsius by 2050.
Even before the climate gets to that point, we may face a dramatic uptick in climate-related disasters, says William Ripple, a distinguished professor of ecology at Oregon State University and the lead author of a recent commentary on the “risky feedback loops” connecting climate-driven systems. There’s a sense of awe—in the original meaning of inspiring terror or dread—at witnessing such sweeping changes play out across the landscape. “Many scientists knew these things would happen, but we’re taken aback by the severity of the major changes we’re seeing,” Ripple said. Armstrong McKay likened the challenge of being a climate scientist in 2023 to that faced by medical professionals: “You put a certain emotional distance between you and the work in order to do the work effectively,” he said, “that can be difficult to maintain.”
Although it may be too late to avert some changes, others could still be staved off by limiting emissions. LeGrande said she worries that talking about tipping points may encourage people to think that any further action now is futile. In fact, the opposite is true, Ripple said. “Scientifically, everything we do to avoid even a tenth of a degree of temperature increase makes a huge difference.”
Climate Collapse Could Happen Fast
Climate Endgame: Exploring catastrophic climate change scenarios
ABSTRACT: Prudent risk management requires consideration of bad-to-worst-case scenarios. Yet, for climate change, such potential futures are poorly understood. Could anthropogenic climate change result in worldwide societal collapse or even eventual human extinction? At present, this is a dangerously underexplored topic. Yet there are ample reasons to suspect that climate change could result in a global catastrophe. Analyzing the mechanisms for these extreme consequences could help galvanize action, improve resilience, and inform policy, including emergency responses. We outline current knowledge about the likelihood of extreme climate change, discuss why understanding bad-to-worst cases is vital, articulate reasons for concern about catastrophic outcomes, define key terms, and put forward a research agenda. The proposed agenda covers four main questions: 1) What is the potential for climate change to drive mass extinction events? 2) What are the mechanisms that could result in human mass mortality and morbidity? 3) What are human societies’ vulnerabilities to climate-triggered risk cascades, such as from conflict, political instability, and systemic financial risk? 4) How can these multiple strands of evidence—together with other global dangers—be usefully synthesized into an “integrated catastrophe assessment”? It is time for the scientific community to grapple with the challenge of better understanding catastrophic climate change.
Climate Endgame: Exploring catastrophic climate change scenarios