Global food prices rise at rapid pace in May 2021 – Food Price Index hits highest value since September 2011, only 7.6 percent below its all-time peak
ROME, 4 June 2021 (FAO) – Global food prices rose in May at their fastest monthly rate in more than a decade, even as world cereal production is on course to reach a new record high, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) reported today.
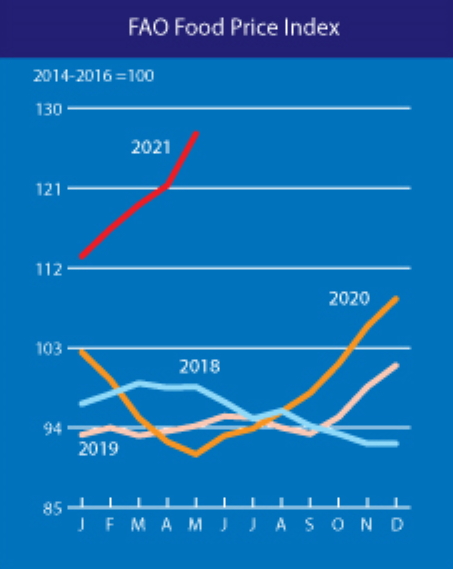
The FAO Food Price Index averaged 127.1 points in May, 4.8 percent higher than in April and 39.7 percent higher than in May 2020.
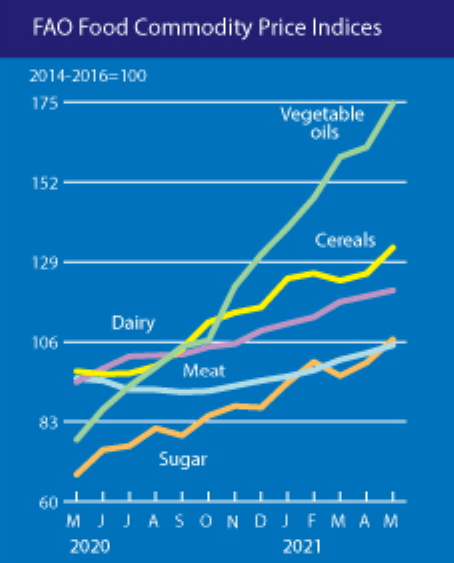
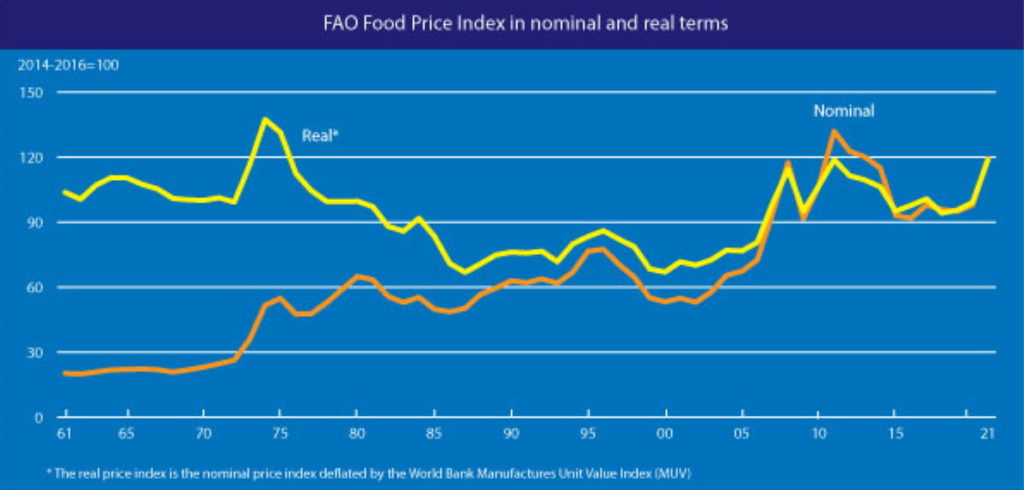
A surge in the international prices of vegetable oils, sugar and cereals led the increase in the index, which tracks monthly changes in the international prices of commonly-traded food commodities, to its highest value since September 2011 and only 7.6 percent below its all-time peak in nominal terms.
The FAO Cereal Price Index increased 6.0 percent from April, led by international maize prices, which averaged 89.9 percent above their year-earlier value. However, maize prices started to retreat at the end of May, mostly on improved production prospects in the United States of America. International wheat prices also showed a late-month decline but averaged 6.8 percent higher in May than in April, while international rice quotations held steady.
The FAO Vegetable Oil Price Index gained 7.8 percent in May, mainly reflecting rising palm, soy and rapeseed oil quotations. Palm oil prices rose due to slow production growth in Southeast Asian countries, while prospects of robust global demand, especially from the biodiesel sector, drove soyoil prices higher.
The FAO Sugar Price Index increased by 6.8 percent from April, due largely to harvest delays and concerns over reduced crop yields in Brazil, the world’s largest sugar exporter, even as large export volumes from India contributed to easing the price surge.
The FAO Meat Price Index increased by 2.2 percent from April, with quotations for all meat types rising due to a faster pace of import purchases by China, as well as rising internal demand for poultry and pig meats in the leading producing regions.
The FAO Dairy Price Index rose by 1.8 percent in the month, averaging 28 percent above its level of one year ago. The increase was led by solid import demand for skim and whole milk powders, while butter prices declined for the first time in almost a year on increased export supplies from New Zealand. [more]