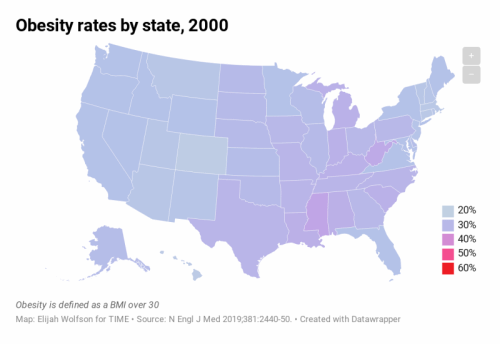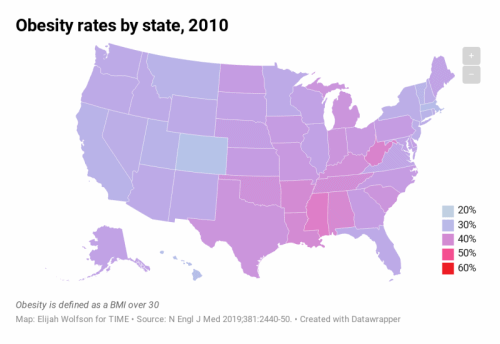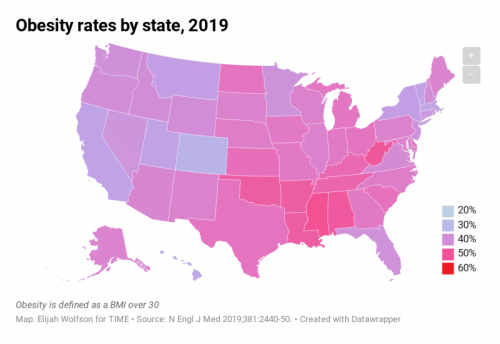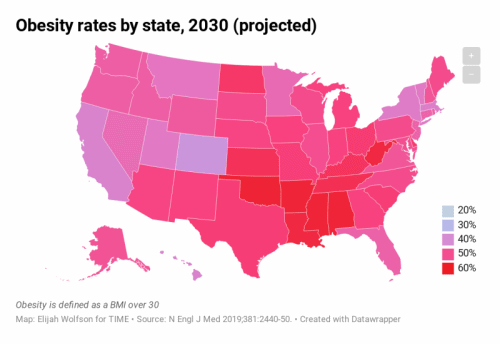
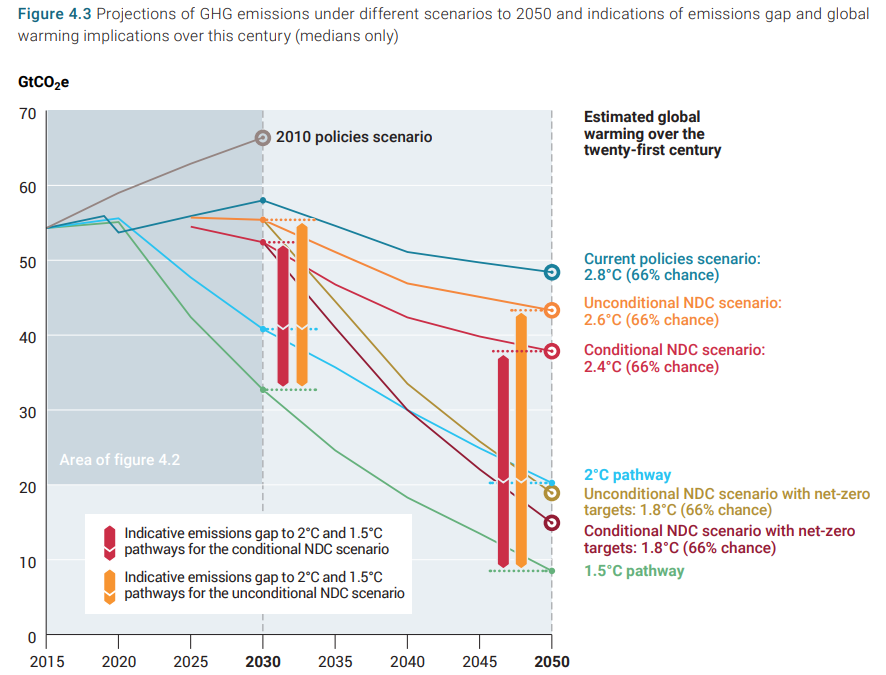
Close to half of U.S. population projected to have obesity by 2030 – “The prevalence of adult obesity and severe obesity will continue to increase nationwide, with large disparities across states and demographic subgroups”
BOSTON, 18 December 2019 (Harvard Chan School) – About half of the adult U.S. population will have obesity and about a quarter will have severe obesity by 2030, according to a new study led by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
The study also predicts that in 29 states, more than half of the population will have obesity, and all states will have a prevalence of obesity higher than 35%. The study’s researchers estimate that, currently, 40% of American adults have obesity and 18% have severe obesity.
The study was published in the 19 December 2019 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine.
The researchers said the predictions are troubling because the health and economic effects of obesity and severe obesity take a toll on several aspects of society. “Obesity, and especially severe obesity, are associated with increased rates of chronic disease and medical spending, and have negative consequences for life expectancy,” said Steven Gortmaker, professor of the practice of health sociology at Harvard Chan School and senior author of the study.
For the study, the researchers used self-reported body mass index (BMI) data from more than 6.2 million adults who participated in the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey (BRFSS) between 1993 and 2016. Body mass index (BMI) is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. Obesity is defined as a BMI of 30 or higher, and severe obesity is a BMI of 35 or higher.
Self-reported BMIs are frequently biased, so the researchers used novel statistical methods to correct for this bias.
The large amount of data collected in the BRFSS allowed the researchers to drill down for obesity rates for specific states, income levels, and subpopulations.
The results showed that by 2030, several states will have obesity prevalence close to 60%, while the lowest states will be approaching 40%. The researchers predicted that nationally, severe obesity will likely be the most common BMI category for women, non-Hispanic black adults, and those with annual incomes below $50,000 per year.
“The high projected prevalence of severe obesity among low-income adults has substantial implications for future Medicaid costs,” said lead author Zachary Ward, programmer/analyst at Harvard Chan School’s Center for Health Decision Science. “In addition, the effect of weight stigma could have far-reaching implications for socioeconomic disparities as severe obesity becomes the most common BMI category among low-income adults in nearly every state.”
Ward and his co-authors said that the study could help inform state policy makers. For example, previous research suggests that sugar-sweetened beverage taxes have been an effective and cost-effective intervention for curtailing the rise in obesity rates. “Prevention is going to be key to better managing this epidemic,” said Ward.
A video of Ward highlighting the results can be found here.
Other Harvard Chan School authors included Sara Bleich, Angie Cradock, Jessica Barrett, Catherine Giles, and Chasmine Flax.
Funding for the study came from the JPB Foundation.
“Projected U.S. State-Level Prevalence of Adult Obesity and Severe Obesity,” Zachary J. Ward, Sara N. Bleich, Angie L. Cradock, Jessica L. Barrett, Catherine M. Giles, Chasmine Flax, Michael W. Long, and Steven L. Gortmaker, New England Journal of Medicine, 19 December 2019, doi:10.1056/NEJMsa1909301.
Contact
- Nicole Rura, 617.432.6141, nrura@hsph.harvard.edu
Close to half of U.S. population projected to have obesity by 2030
Projected U.S. State-Level Prevalence of Adult Obesity and Severe Obesity
ABSTRACT: Although the national obesity epidemic has been well documented, less is known about obesity at the U.S. state level. Current estimates are based on body measures reported by persons themselves that underestimate the prevalence of obesity, especially severe obesity.
We developed methods to correct for self-reporting bias and to estimate state-specific and demographic subgroup–specific trends and projections of the prevalence of categories of body-mass index (BMI). BMI data reported by 6,264,226 adults (18 years of age or older) who participated in the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey (1993–1994 and 1999–2016) were obtained and corrected for quantile-specific self-reporting bias with the use of measured data from 57,131 adults who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. We fitted multinomial regressions for each state and subgroup to estimate the prevalence of four BMI categories from 1990 through 2030: underweight or normal weight (BMI [the weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters], <25), overweight (25 to <30), moderate obesity (30 to <35), and severe obesity (≥35). We evaluated the accuracy of our approach using data from 1990 through 2010 to predict 2016 outcomes.
The findings from our approach suggest with high predictive accuracy that by 2030 nearly 1 in 2 adults will have obesity (48.9%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 47.7 to 50.1), and the prevalence will be higher than 50% in 29 states and not below 35% in any state. Nearly 1 in 4 adults is projected to have severe obesity by 2030 (24.2%; 95% CI, 22.9 to 25.5), and the prevalence will be higher than 25% in 25 states. We predict that, nationally, severe obesity is likely to become the most common BMI category among women (27.6%; 95% CI, 26.1 to 29.2), non-Hispanic black adults (31.7%; 95% CI, 29.9 to 33.4), and low-income adults (31.7%; 95% CI, 30.2 to 33.2).
Our analysis indicates that the prevalence of adult obesity and severe obesity will continue to increase nationwide, with large disparities across states and demographic subgroups. (Funded by the JPB Foundation.)
Projected U.S. State-Level Prevalence of Adult Obesity and Severe Obesity