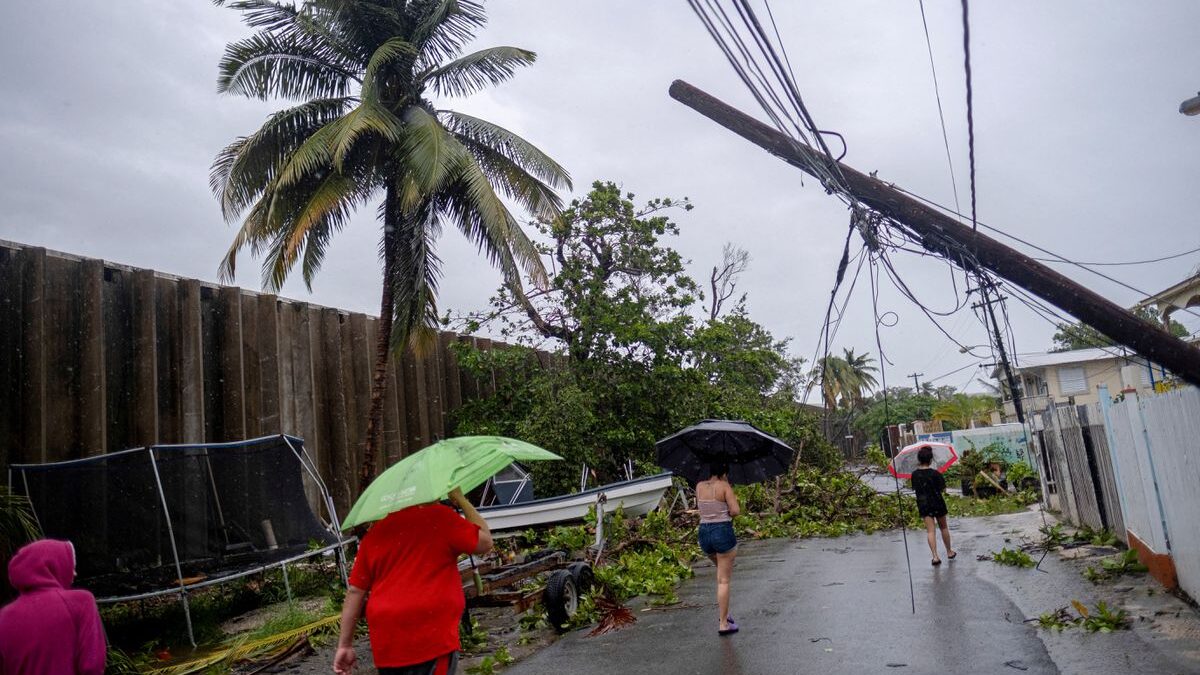
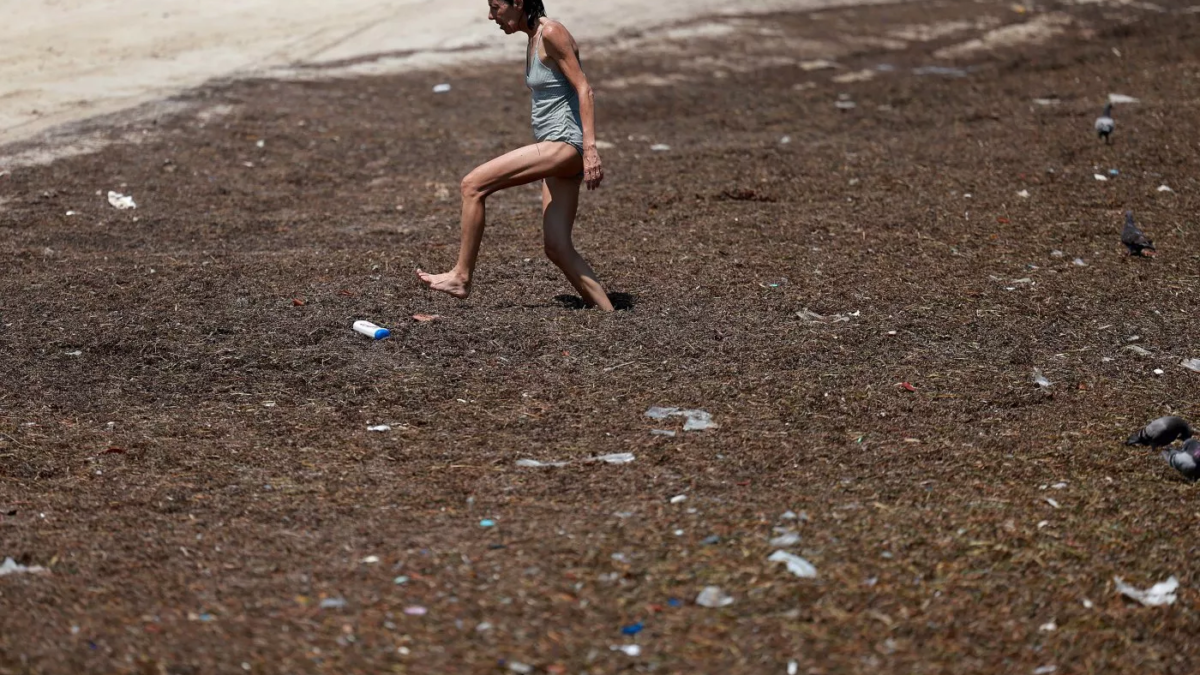
Leaving microbes out of climate change conversation has major consequences, experts warn – “Climate change is literally starving ocean life”

By Ivy Shih
19 June 2019
(UNSW) – An international group of leading microbiologists have issued a warning, saying that not including microbes – the support system of the biosphere – in the climate change equation will have major negative flow-on effects.
More than 30 microbiologists from 9 countries have issued a warning to humanity – they are calling for the world to stop ignoring an ‘unseen majority’ in Earth’s biodiversity and ecosystem when addressing climate change.
‘Scientist’s warning to humanity: microorganisms and climate change’ was published today in the journal Nature Reviews Microbiology. Professor Rick Cavicchioli, microbiologist at the School of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences at UNSW Sydney, has led the global effort.
With their statement, the researchers are hoping to raise awareness both for how microbes can influence climate change and how they will be impacted by it – calling for including microbes in climate change research, increasing the use of research involving innovative technologies, and improving education in classrooms.
“Micro-organisms, which include bacteria and viruses, are the lifeforms that you don’t see on the conservation websites,” says Professor Cavicchioli.
“They support the existence of all higher lifeforms and are critically important in regulating climate change.
“However, they are rarely the focus of climate change studies and not considered in policy development.”
Professor Cavicchioli calls microbes the ‘unseen majority’ of lifeforms on earth, playing critical functions in animal and human health, agriculture, the global food web and industry.
This goes to the heart of climate change, so if micro-organisms aren’t considered effectively it means models cannot be generated properly and predictions could be inaccurate.
Professor Rick Cavicchioli, School of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences at UNSW Sydney
For example, the Census of Marine Life estimates that 90% of the ocean’s total biomass is microbial. In our oceans, marine lifeforms called phytoplankton take light energy from the sun and remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as much as plants. The tiny phytoplankton form the beginning of the ocean food web, feeding krill populations that then feed fish, sea birds and large mammals such as whales.
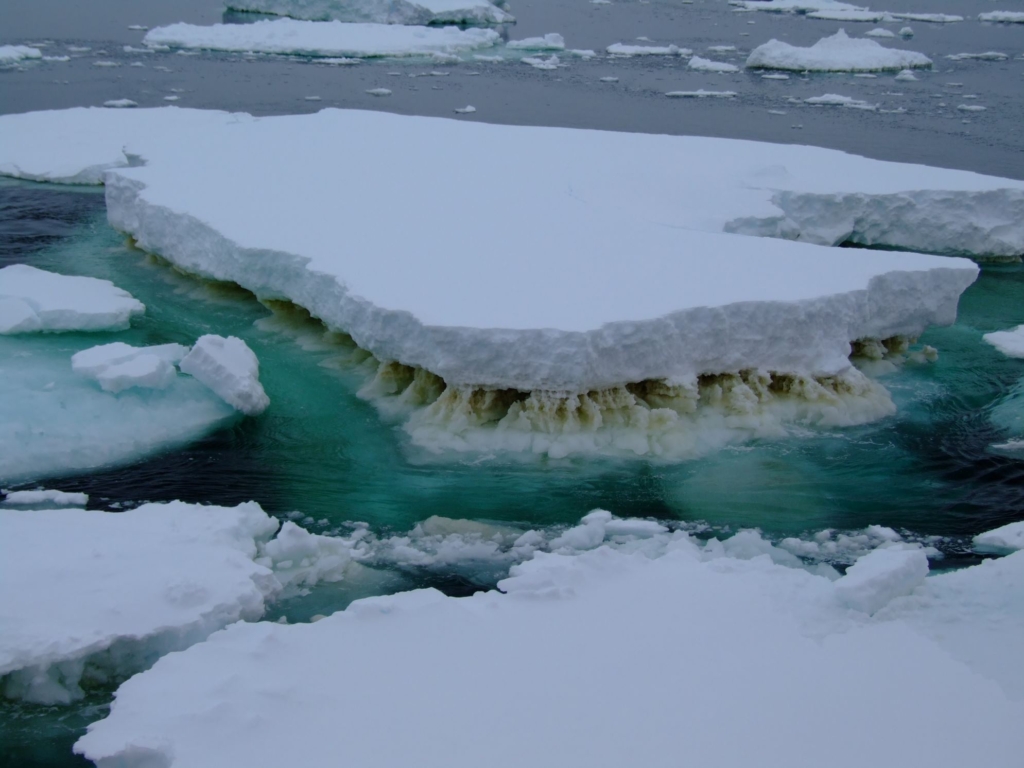
Sea ice algae thrive in sea ice ‘houses’. If global warming trends continue, the melting sea ice has a downstream effect on the sea ice algae, which means a diminished ocean food web.
“Climate change is literally starving ocean life,” says Professor Cavicchioli.
Beyond the ocean, microbes are also critical to terrestrial environments, agriculture and disease.
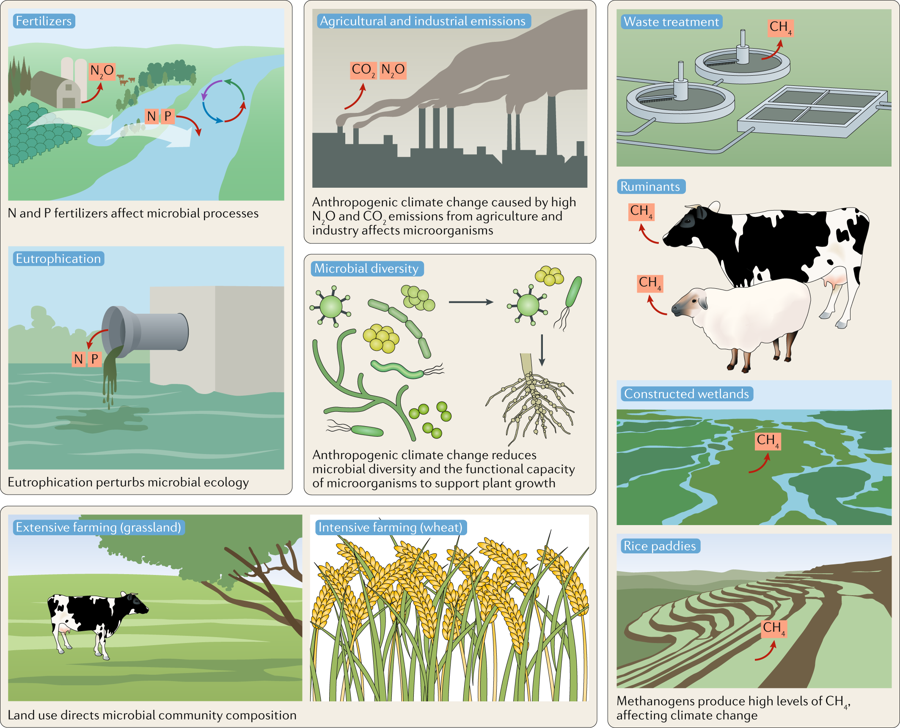
“In terrestrial environments, microbes release a range of important greenhouse gases to the atmosphere (carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide), and climate change is causing these emissions to increase,” Professor Cavicchioli says.
“Farming ruminant animals releases vast quantities of methane from the microbes living in their rumen – so decisions about global farming practices need to consider these consequences.
“And lastly, climate change worsens the impact of pathogenic microbes on animals (including humans) and plants – that’s because climate change is stressing native life, making it easier for pathogens to cause disease.
“Climate change also expands the number and geographic range of vectors (such as mosquitos) that carry pathogens. The end result is the increased spread of disease, and serious threats to global food supplies.”
Greater commitment to microbe-based research needed
In their statement, the scientists call on researchers, institutions and governments to commit to greater microbial recognition to mitigate climate change.
“The statement emphasises the need to investigate microbial responses to climate change and to include microbe-based research during the development of policy and management decisions,” says Professor Cavicchioli.
Additionally, climate change research that links biological processes to global geophysical and climate processes should have a much bigger focus on microbial processes.

“This goes to the heart of climate change, so if micro-organisms aren’t considered effectively it means models cannot be generated properly and predictions could be inaccurate,” says Professor Cavicchioli.
“Decisions that are made now impact on humans and other forms of life, so if you don’t take into account the microbial world, you’re missing a very big component of the equation.”
Professor Cavicchioli says that microbiologists are also working on developing resources that will be made available for teachers to educate students on the importance of microbes.
“If that literacy is there, that means people will have a much better capacity to engage with things to do with microbiology and understand the ramifications and importance of microbes.”
Microbiologists can endorse the researchers’ warning by becoming a signatory here: https://www.babs.unsw.edu.au/research/microbiologists-warning-humanity
Leaving microbes out of climate change conversation has major consequences, experts warn
ABSTRACT: In the Anthropocene, in which we now live, climate change is impacting most life on Earth. Microorganisms support the existence of all higher trophic life forms. To understand how humans and other life forms on Earth (including those we are yet to discover) can withstand anthropogenic climate change, it is vital to incorporate knowledge of the microbial ‘unseen majority’. We must learn not just how microorganisms affect climate change (including production and consumption of greenhouse gases) but also how they will be affected by climate change and other human activities. This Consensus Statement documents the central role and global importance of microorganisms in climate change biology. It also puts humanity on notice that the impact of climate change will depend heavily on responses of microorganisms, which are essential for achieving an environmentally sustainable future.
Scientists’ warning to humanity: microorganisms and climate change


