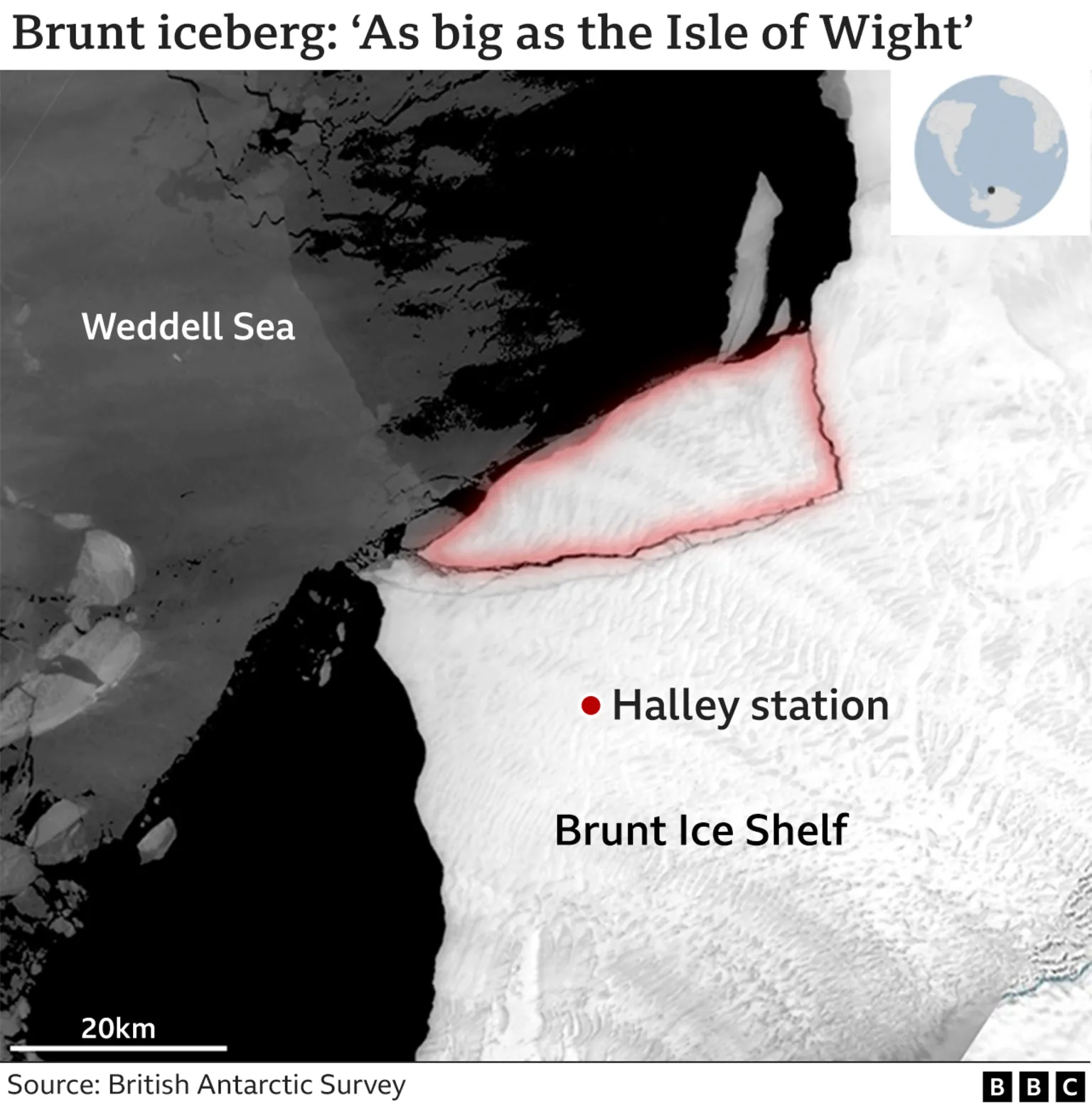
Isle of Wight-size iceberg breaks from Antarctica – “This latest calving reduces the Brunt Ice Shelf to its smallest observed size”
By Jonathan Amos
21 May 2024
(BBC News) – Another big iceberg has broken away from an area of the Antarctic that hosts the UK’s Halley research station.
It is the third such block to calve near the base in the past three years.
This new one is not quite as large, but still measures some 380 sq km (145 sq miles) – roughly the size of the Isle of Wight.
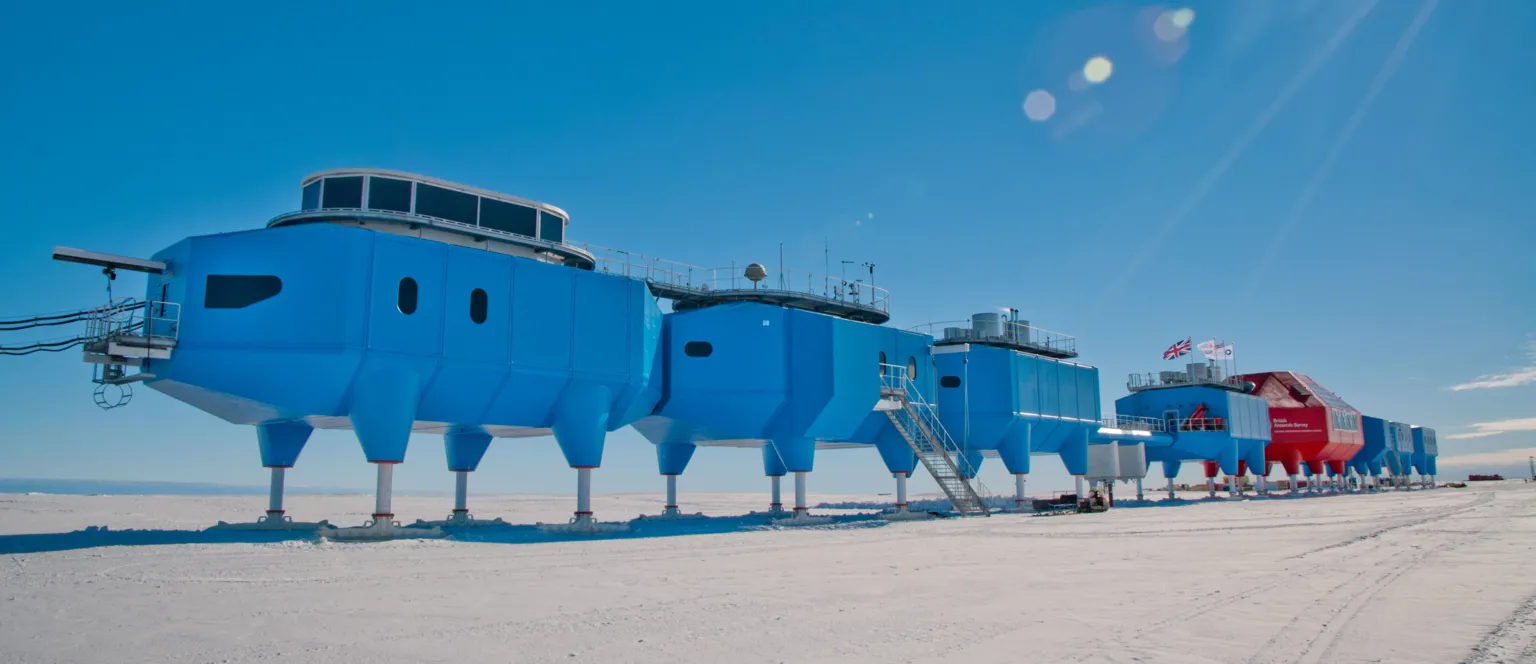
The British Antarctic Survey (BAS) took the precaution of moving Halley in 2017 because of concerns over the way the local ice was behaving.
Its buildings were shifted on skis to take them away from immediate trouble.
The station is also now routinely vacated during the long dark months of the southern winter. The last personnel were flown out in February.
Halley sits on top of the Brunt Ice Shelf, which is the floating protrusion of glaciers that have flowed off the continent into the Weddell Sea.

This shelf will periodically shed icebergs at its forward edge and it is currently going through an extremely dynamic phase.
In 2021, the shelf produced a berg the size of Greater Paris (1,300 sq km/810 sq miles) called A74, followed in 2023 by an even bigger block (1,500 sq km/930 sq miles) the size of Greater London, known as A81.
The origin of the new berg goes back to a major crack that was discovered in the shelf on 31 October, 2016. Predictably, it was nicknamed the “Halloween Crack”.
A further fracture perpendicular to Halloween has now cut a free-floating segment of ice that has already begun to drift out into the Weddell Sea. […]
The loss of so much ice from the Brunt structure these past three years has triggered a rapid acceleration in the shelf’s seaward movement.
Historically, it has flowed forward at a rate of 400-800m (1,300-2,600ft) per year. It is now moving at about 1,300m (4,300ft) a year. […]
“This latest calving reduces the Brunt Ice Shelf to its smallest observed size,” commented remote sensing specialist Prof Adrian Luckman, from Swansea University.
“Since the calving of Iceberg A81 in January 2023, the ice shelf is also more dynamically active than previous years. We may be observing the end of a dynamic readjustment, but only time will tell if things settle down now.” [more]