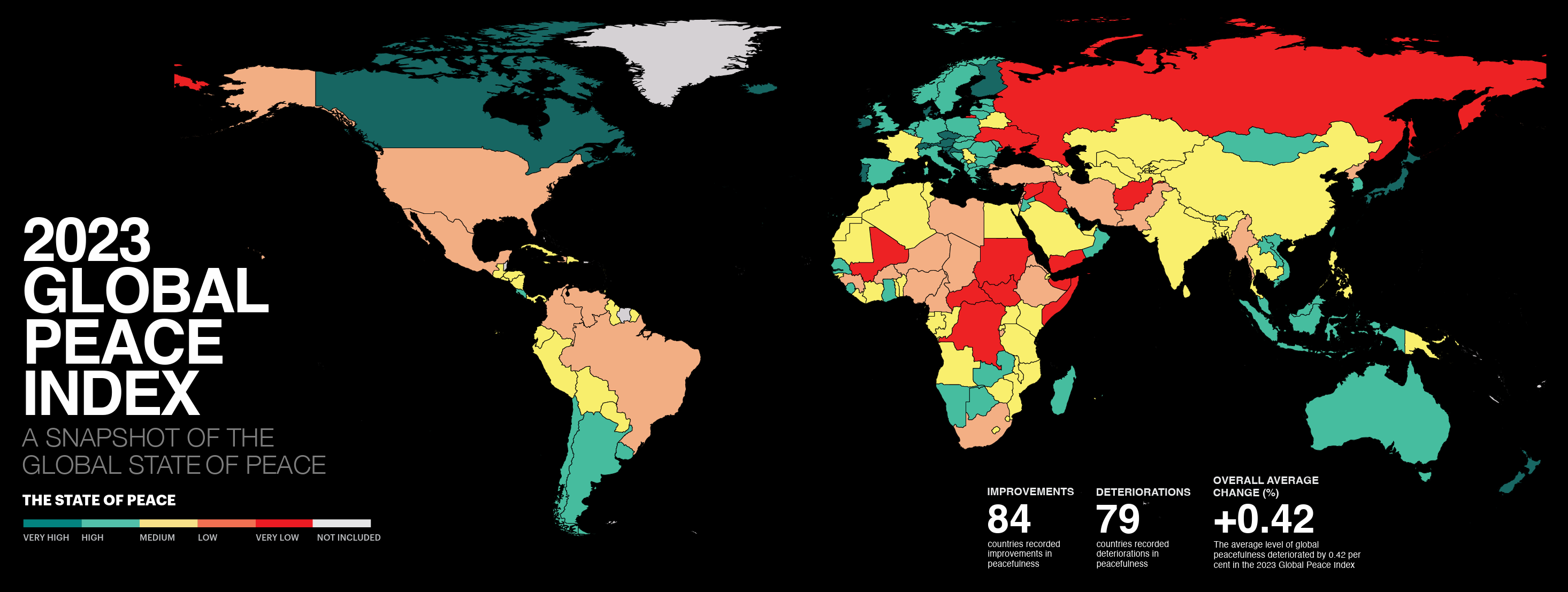
Conflict deaths in 2023 at highest level this century – Conflicts are becoming more internationalised, with 91 countries now involved in some form of external conflict, up from 58 in 2008
LONDON, 28 June 2023 (IEP) – Today marks the launch of the 17th edition of the Global Peace Index from international think-tank, the Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP).
Key results
- Deaths from global conflict increased by 96% to 238,000.
- New data shows higher number of conflict deaths in Ethiopia than Ukraine, eclipsing the previous global peak during the Syrian war.
- 79 countries witnessed increased levels of conflict including Ethiopia, Myanmar, Ukraine, Israel, and South Africa.
- The global economic impact of violence increased by 17% or $1 trillion, to $17.5 trillion in 2022, equivalent to 13% of global GDP.
- A Chinese blockade of Taiwan would cause a drop in global economic output of $2.7 trillion, almost double the loss that occurred due to the 2008 global financial crisis.
- Despite the conflict in Ukraine, 92 countries improved on military expenditure and 110 decreased their military personnel.
- Conflicts are becoming more internationalised with 91 countries now involved in some form of external conflict, up from 58 in 2008.
Impact of the war in Ukraine on peacefulness
- Ukraine recorded the largest deterioration, falling 14 places to 157th.
- The economic impact of violence has increased by 479% or $449 billion, equivalent to 64% of Ukraine’s GDP.
- Despite the conflict, Russia’s incarceration rate, violent demonstrations, terrorism impact and homicide rates have improved over the past year, with the homicide rate at its lowest since 2008.
- 65% of men in Ukraine aged 20 to 24 years have fled the country or died in the conflict.
The 17th edition of the annual Global Peace Index (GPI) [pdf], the world’s leading measure of peacefulness, reveals the average level of global peacefulness deteriorated for the ninth consecutive year, with 84 countries recording an improvement and 79 a deterioration. This demonstrates that the deteriorations were larger than the improvements, as the post-COVID rises of civil unrest and political instability remain high while regional and global conflicts accelerate.
Iceland remains the most peaceful country, a position it has held since 2008, followed by Denmark, Ireland, New Zealand and Austria. For the sixth consecutive year, Afghanistan is the least peaceful country, followed by Yemen, Syria, South Sudan, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Highlighting the shifting dynamics of conflict, both Afghanistan and Syria recorded improvements in peacefulness.
Ukraine’s overall score recorded a decline of 13%, the largest deterioration in the 2023 GPI, and is now 157th on the Index. Libya experienced the largest improvement in overall peacefulness, improving by 7% and rising 14 places to 137th.
The shift in the global distribution of conflict continued as major conflicts in the MENA region and South Asia declined, while conflicts in sub-Saharan Africa, Europe, and Asia-Pacific intensified. The Russia and Eurasia region recorded the largest deterioration in peacefulness in the world.
Ten of the 23 GPI indicators improved, 11 deteriorated, and two had no change. The largest deteriorations were in External Conflicts Fought and Deaths from Internal Conflict. Other notable deteriorations included Neighbouring Country Relations and Political Instability, where 59 countries deteriorated.
The impact of violence on the global economy increased by $1 trillion to a record $17.5 trillion. This is equivalent to 13% of global GDP, approximately $2,200 per person. This was due to increased military expenditure owing to the Ukraine war. The disparity in the economic impact of violence is stark: the ten countries most affected averaged 34% of GDP, compared to just 3% for the ten least affected.
Steve Killelea, Founder & Executive Chairman of IEP, said: “The 2023 Global Peace Index highlights the contrasting dynamics of militarisation and conflict. On the one hand, the majority of countries are decreasing their reliance on the military, while on the other hand an increasing number of conflicts are becoming internationalised. Conflict deaths are the highest since the Rwandan genocide which had over 800,000 deaths and sparked a wave of global action.”
“After the Afghanistan, Iraq, and Syrian wars and now the Ukraine war it is obvious that the most powerful armies cannot prevail against a well-resourced local population. War has become mostly unwinnable, and an increasingly heavy economic burden. This is highlighted by the impact of a potential economic blockade on Taiwan, which would result in a global economic recession twice as impactful as the global financial crisis of 2008.”
The rise in conflicts
79 countries deteriorated in the Ongoing Conflict domain, with conflict related deaths increasing by 96% compared to the prior year. Conflict deaths are now at the highest level this century. The Ethiopian conflict claimed the most lives in 2022 with new data finding that battlefield deaths were over 100,000, while disease and famine related deaths were conservatively estimated at over 200,000. This conflict has been largely hidden from the media because of domestic media restrictions and internet blackouts. This has coincided with US and UN aid organisations stopping food shipments because of corruption in the food supply chains.
In sub-Saharan Africa, Mali recorded the largest deterioration with conflict-related deaths increasing by 154%, while violence against civilians rose by 570%. Eswatini experienced the next largest drop in peacefulness in the region.
The Ukraine war has seen the total number of Ukrainians who were either refugees or internally displaced jump from 1.7% before the conflict, to over 30% and is likely to continue increasing. Recent data has found that up to 65% of men in Ukraine aged 20 to 24 years have fled the country or died in the conflict. The report estimates 83,000 deaths are related to the conflict so far.
In contrast to the devastating effects of the war on the Russian population, other internal factors have improved including the incarceration rate, a decrease in violent demonstrations, and the impact of terrorism. The homicide rate within Russia is now at its lowest level since the inception of the GPI in 2008. If not for the Ukraine conflict, Russia would have been one of the largest improvers in peace in this year’s Index.
The global number of refugees and internally displaced people continues to rise; there are now 15 countries with over 5% of their population displaced. [more]