From Ukraine to Yemen, UN seeks record $51.5 billion for “shockingly high” aid needs – “The humanitarian response system is being tested to its limits”

By Emma Farge
1 December 2022
GENEVA (Reuters) – The United Nations and partners on Thursday appealed for a record $51.5 billion in aid money for 2023, with tens of millions of additional people expected to need assistance, testing the humanitarian response system “to its limits”.
The appeal represents a 25% increase on 2022 and is more than five times the amount sought a decade ago.
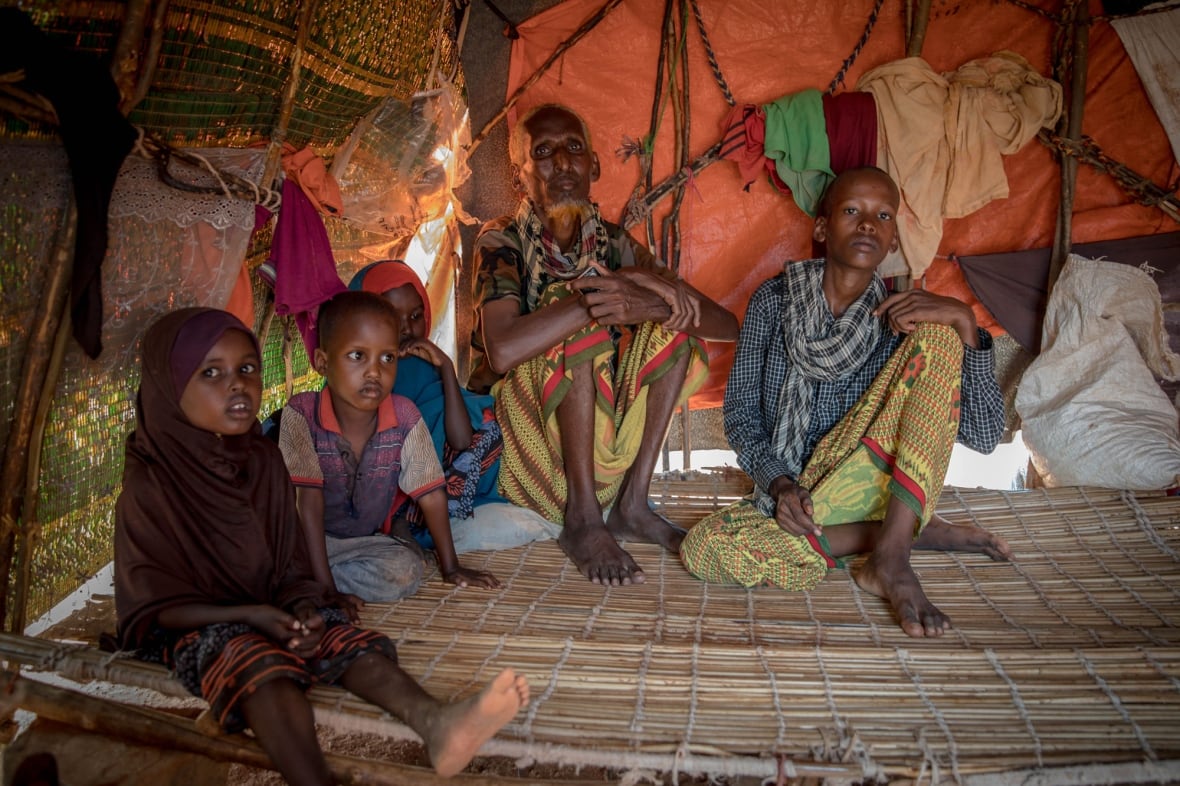
The U.N. Global Humanitarian Overview estimates that an extra 65 million people will need help next year, bringing the total to 339 million in 68 countries.
That represents more than 4% of the people on the planet or about the population of the United States.
For the first time ever, ten countries have individual appeals of more than $1 billion: Afghanistan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Somalia, Sudan, South Sudan, Syria, Ukraine, and Yemen.
“Humanitarian needs are shockingly high, as this year’s extreme events are spilling into 2023,” said U.N. Emergency Relief Coordinator Martin Griffiths, citing the war in Ukraine and drought in the Horn of Africa.
“For people on the brink, this appeal is a lifeline.”

Over 100 million people have been driven from their homes as conflict and climate change fuel a displacement crisis.
Nine months of war between Russia and Ukraine have disrupted food exports and around 45 million people in 37 countries are currently facing starvation, the report said.
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to major setbacks in child vaccination programmes and thwarted efforts to end extreme poverty, fuelling other diseases such as cholera, Griffiths said at the launch on Thursday.
For the first time ever, ten countries have individual appeals of more than $1 billion – Afghanistan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Somalia, Sudan, South Sudan, Syria, Ukraine, and Yemen.
But donor funding is already under strain with the multiple crises, forcing aid workers to make tough decisions on priorities.

The United Nations faces the biggest funding gap ever, with its unmet funding at 53% in 2022, based on data through to mid-November.
“The humanitarian response system is being tested to its limits,” Griffiths said.
Unlike in other parts of the U.N. where fees depend on countries’ economic size, humanitarian funding is voluntary and relies overwhelmingly on Western donations.
The United States is by far the biggest donor, giving over $14 billion so far this year, followed by Germany and the European Commission while other major economies like China and India have given less than $10 million each.
From Ukraine to Yemen, UN seeks record $51.5 bln for ‘shockingly high’ aid needs