A shrinking Lake Powell heralds an even worse water crisis in the Southwest’s future – “These trends are on a tragic collision course, underscoring the urgency once again of concerted action on climate”

By Matthew Rozsa
29 August 2022
(Salon) – As climate change worsens, Americans who live in the Southwest will be hit very, very hard: experts predict that large cities like Phoenix and Las Vegas are going to be uninhabitable within decades, as will the surrounding metropolitan areas in their home states of Arizona and Nevada. Those regions are expected to overheat, like an oven with a temperature that constantly rises; by contrast, as the water cycle intensifies, there is apt to be more flash floods like the ones which already occurred in St. Louis, Mo. and throughout the state of Kentucky.
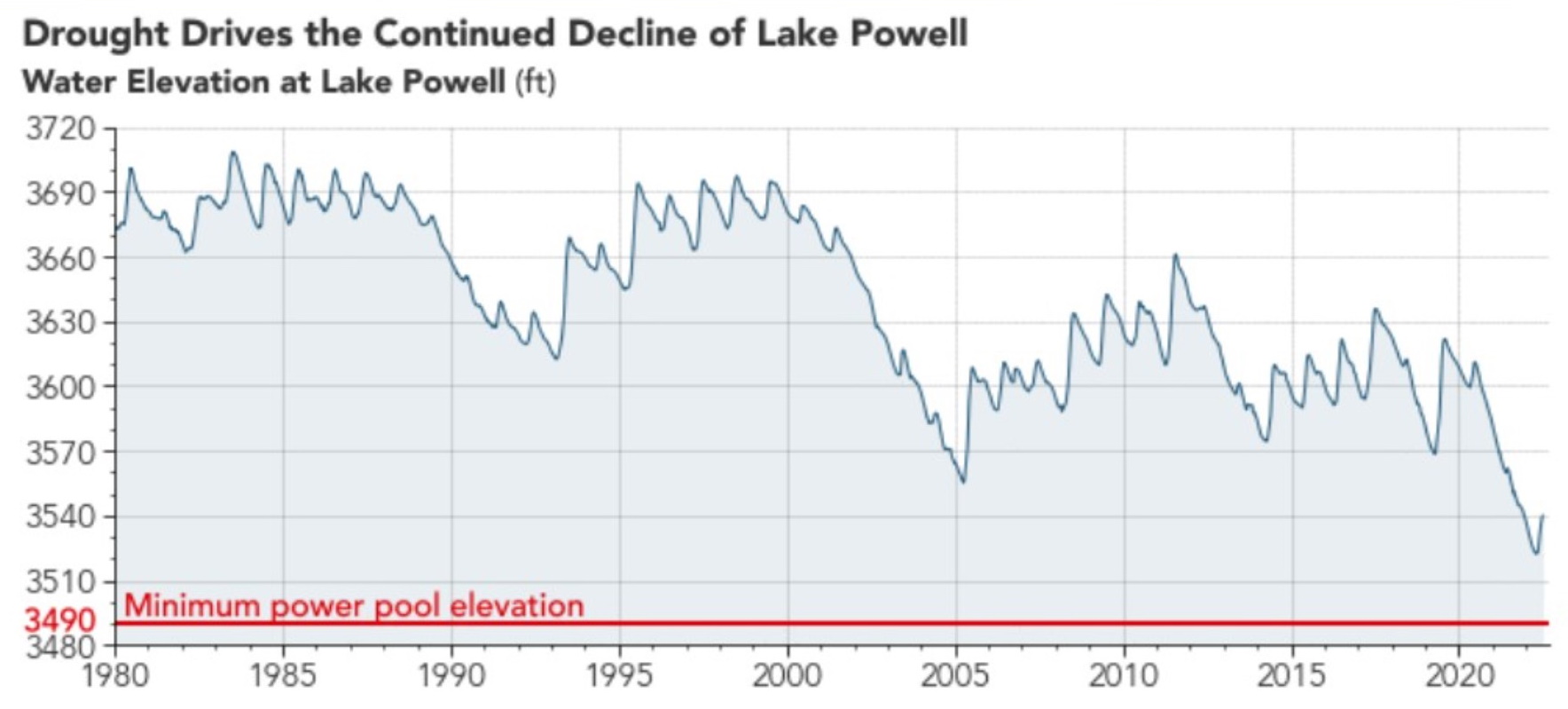
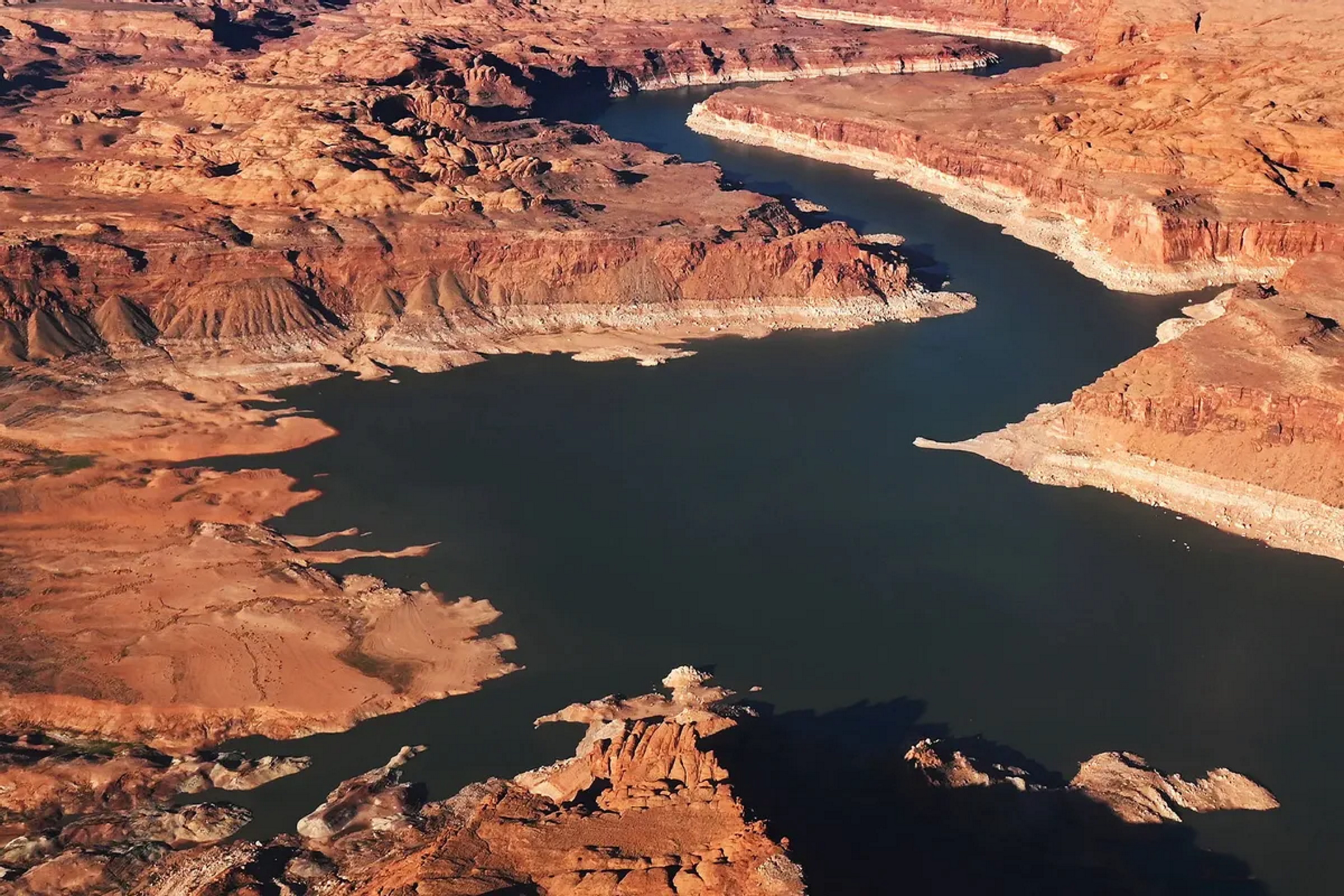
Already, there are some omens pointing to the Southwest’s harsh future: in particular, Lake Powell, the second largest artificial reservoir in the United States, at least, in terms of its maximum water capacity. Connected to the Colorado River, Lake Powell provides water and electricity (through hydroelectric power) to 4 to 5 million acres of southwestern farmland, the metropolitan areas of Phoenix and Las Vegas, and the Los Angeles and San Diego metropolises — the two largest metropolitan areas of southern California.
That is why experts are so concerned by the news that Lake Powell is shrinking. As of late August, Lake Powell is filled to only 26 percent of its capacity, the smallest it has been since 1967. Just as sobering, nearby Lake Mead is only at 28 percent of its capacity, while the Colorado River system is only at 34 percent.
The low water levels across these reservoirs are a direct consequence of man-made climate change, scientists attest.
“The connection is direct,” Dr. Michael E. Mann, a distinguished professor of atmospheric science at Penn State University, told Salon by email. “The aridification of the western U.S. Is a long-predicted consequence of human caused warming. The drop in levels of Lake Mead and Lake Powell are very clear indicators of this trend because they integrate the hydrological balance over many years.”
Daniel L. Swain, PhD, a climate scientist at the Institute of the Environment & Sustainability at the University of California, Los Angeles, wrote to Salon that climate change can be blamed for roughly 40% to 50% of the severity of the megadrought currently afflicting the Southwest. He mainly attributed this to the rising temperatures themselves, as the increased heat causes the atmosphere to suck more water up and reduces the amount of mountain precipitation that falls as snow.
“The shrinking of Lake Powell is due to a number of factors, including the climate change-induced drying noted above, increasing human demand for water in the Basin, and various specific water and dam operation decisions over the years,” Swain explained. “The net effect is that there’s far more demand for Colorado River water than there is actual water in the Colorado River system at this point — and the gap continues to widen as supply dwindles and demand rises”
The undersupply of water is going to have a dire effect on the roughly 60 million people who inhabit that part of the country. According to Ali S. Akanda, an associate professor and graduate director of civil and environmental engineering at the University of Rhode Island, the situation has already affected Lake Powell’s appeal as a tourist and recreational site — “for example, the Grand Canyon National Park and the famous river exploration activities are all dependent on water releases from Lake Powell.” But that is just the tip of the iceberg.
“A more significant impact will be on the native reservation communities (Navajo and others) in this dry and arid Lake Powell watershed, who have very limited water infrastructure to begin with,” Akanda told Salon. “Their sources of income, customs, culture, and overall way of life will be deeply impacted if the lake dries up entirely.” He also noted that the water in that area is “hotly contested,” and many highly populated regions will suffer if there is less water.
“A drying Lake Powell will also mean the downstream users in Arizona and Mexico will have no more water flowing from the upstream,” Akanda told Salon, adding that Los Angeles gets approximately 20% of its water from the Lake Powell region. This will have a negative effect on “agriculture, power production, fisheries and ecosystems across the southern part of the Colorado basin,” Akanda noted.
Mann said that the American west will suffer as water dries up.
“It will become increasingly difficult for people in the western US to meet their freshwater needs as supply continues to decrease and population and demand increase,” Mann told Salon. “These trends are on a tragic collision course, underscoring the urgency once again of concerted action on climate.” [more]
A shrinking Lake Powell could herald an even worse water crisis in the Southwest’s future