U.S. sinks to new low in ranking of world’s democracies, slipping 11 points in a decade, below Argentina and Mongolia – “These longer-term challenges aren’t going to be addressed with quick fixes. A change of president is not gonna make them go away”
By Sam Levine
24 March 2021
(The Guardian) – The US has fallen to a new low in a global ranking of political rights and civil liberties, a drop fueled by unequal treatment of minority groups, damaging influence of money in politics, and increased polarization, according to a new report by Freedom House, a democracy watchdog group.
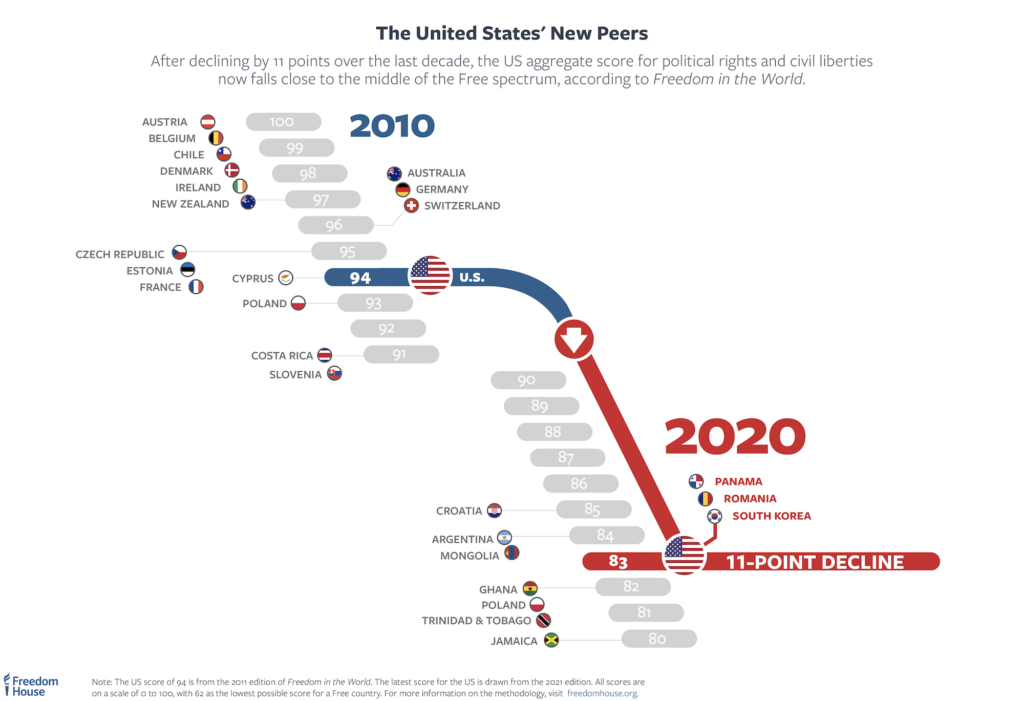
The US earned 83 out of 100 possible points this year in Freedom House’s annual rankings of freedoms around the world, an 11-point drop from its ranking of 94 a decade ago. The US’s new ranking places it on par with countries like Panama, Romania and Croatia and behind countries such as Argentina and Mongolia. It lagged far behind countries like the United Kingdom (93), Chile (93), Costa Rica (91) and Slovakia (90).
“Dropping 11 points is unusual, especially for an established democracy, because they tend to be more stable in our scores,” Sarah Repucci, Freedom House’s vice-president for research and analysis, told the Guardian. “It’s significant for Americans and it’s significant for the world, because the United States is such a prominent, visible democracy, one that is looked to for so many reasons.”
While Freedom House has long included the US in its global ranking of freedoms, it traditionally has not turned an eye inward and focused on US democracy. But this year, Repucci authored an extensive report doing just that, a move motivated by increasing concern over attacks on freedoms in the US.
The report details the inequities that minority groups, especially Black people and Native Americans face when it comes to the criminal justice system and voting. It also illustrates that public trust in government has been damaged by the way rich Americans can use their money to exert outsize influence on American politics.
And it points out that extreme partisan gerrymandering – the manipulation of electoral district lines to boost one party over the other – has contributed to dramatic polarization in the US, threatening its democratic foundations. Gerrymandering, the report says, “has the most corrosive and radicalizing effect on US politics”.
“We’re really concerned about these longer-term challenges that aren’t going to be addressed with quick fixes, that were kind of highlighted during the Trump administration and, in some cases, taken advantage of, by that administration.” Repucci said. “A change of president is not gonna make them go away.” [more]