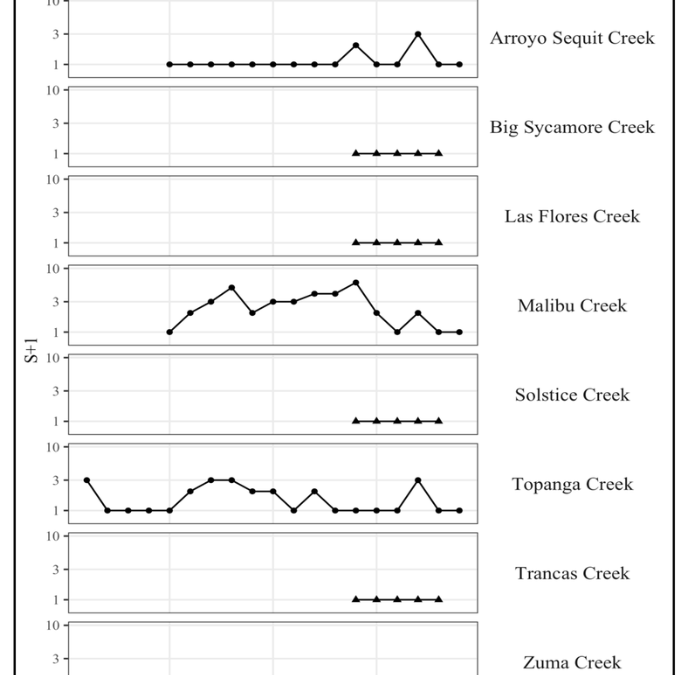
The looming bank collapse – “This crisis is more horrifying than I anticipated”

By Frank Partnoy
14 June 2020
(The Atlantic) – After months of living with the coronavirus pandemic, American citizens are well aware of the toll it has taken on the economy: broken supply chains, record unemployment, failing small businesses. All of these factors are serious and could mire the United States in a deep, prolonged recession. But there’s another threat to the economy, too. It lurks on the balance sheets of the big banks, and it could be cataclysmic. Imagine if, in addition to all the uncertainty surrounding the pandemic, you woke up one morning to find that the financial sector had collapsed.
You may think that such a crisis is unlikely, with memories of the 2008 crash still so fresh. But banks learned few lessons from that calamity, and new laws intended to keep them from taking on too much risk have failed to do so. As a result, we could be on the precipice of another crash, one different from 2008 less in kind than in degree. This one could be worse. […]
I was part of the group that structured and sold CDOs and CLOs at Morgan Stanley in the 1990s. The two securities are remarkably alike. Like a CDO, a CLO has multiple layers, which are sold separately. The bottom layer is the riskiest, the top the safest. If just a few of the loans in a CLO default, the bottom layer will suffer a loss and the other layers will remain safe. If the defaults increase, the bottom layer will lose even more, and the pain will start to work its way up the layers. The top layer, however, remains protected: It loses money only after the lower layers have been wiped out.
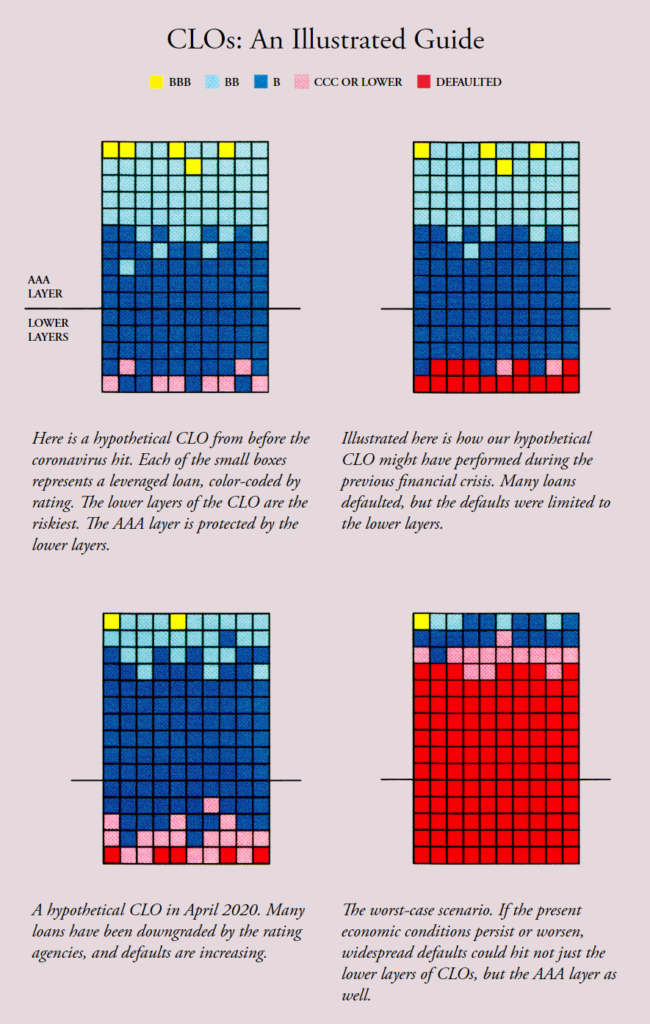
Unless you work in finance, you probably haven’t heard of CLOs, but according to many estimates, the CLO market is bigger than the subprime-mortgage CDO market was in its heyday. The Bank for International Settlements, which helps central banks pursue financial stability, has estimated the overall size of the CDO market in 2007 at $640 billion; it estimated the overall size of the CLO market in 2018 at $750 billion. More than $130 billion worth of CLOs have been created since then, some even in recent months. Just as easy mortgages fueled economic growth in the 2000s, cheap corporate debt has done so in the past decade, and many companies have binged on it.
Despite their obvious resemblance to the villain of the last crash, CLOs have been praised by Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell and Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin for moving the risk of leveraged loans outside the banking system. Like former Fed Chair Alan Greenspan, who downplayed the risks posed by subprime mortgages, Powell and Mnuchin have downplayed any trouble CLOs could pose for banks, arguing that the risk is contained within the CLOs themselves.
These sanguine views are hard to square with reality. The Bank for International Settlements estimates that, across the globe, banks held at least $250 billion worth of CLOs at the end of 2018. Last July, one month after Powell declared in a press conference that “the risk isn’t in the banks,” two economists from the Federal Reserve reported that U.S. depository institutions and their holding companies owned more than $110 billion worth of CLOs issued out of the Cayman Islands alone. A more complete picture is hard to come by, in part because banks have been inconsistent about reporting their CLO holdings. The Financial Stability Board, which monitors the global financial system, warned in December that 14 percent of CLOs—more than $100 billion worth—are unaccounted for.
I have a checking account and a home mortgage with Wells Fargo; I decided to see how heavily invested my bank is in CLOs. I had to dig deep into the footnotes of the bank’s most recent annual report, all the way to page 144. Listed there are its “available for sale” accounts. These are investments a bank plans to sell at some point, though not necessarily right away. The list contains the categories of safe assets you might expect: U.S. Treasury bonds, municipal bonds, and so on. Nestled among them is an item called “collateralized loan and other obligations”—CLOs. I ran my finger across the page to see the total for these investments, investments that Powell and Mnuchin have asserted are “outside the banking system.”
The total is $29.7 billion. It is a massive number. And it is inside the bank. [more]