Ecuador reaches fuel subsidy deal to end violent protests

By Chris Arnold
14 October 2019
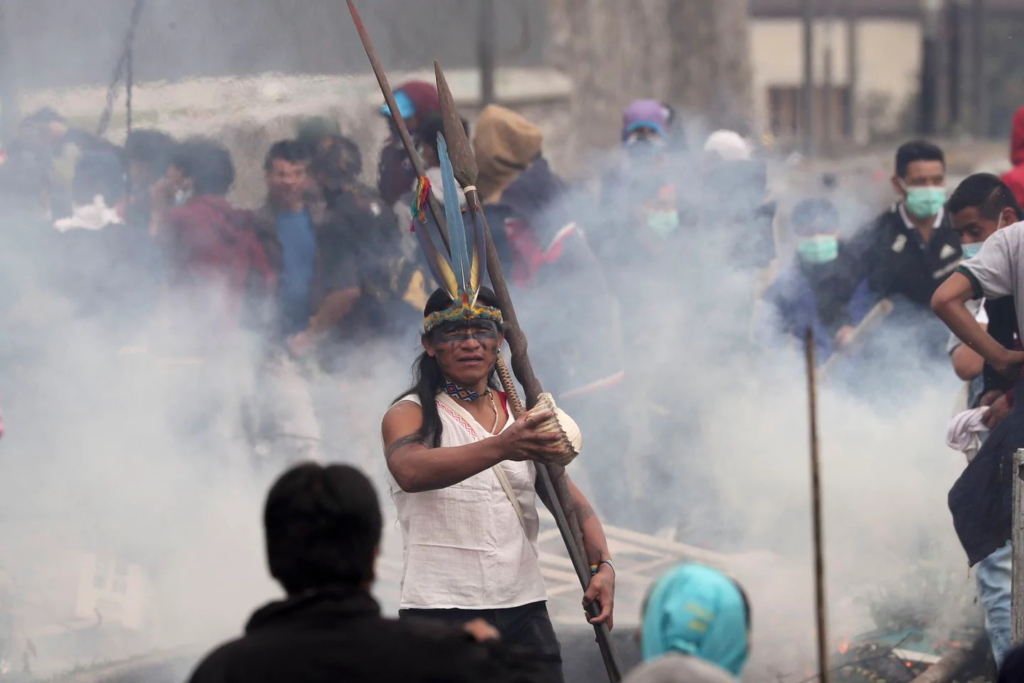
(NPR) – Ecuadorian President Lenin Moreno and leaders of the country’s indigenous peoples have reached a deal to cancel a disputed austerity package. The move follows nearly two weeks of violent, widespread protests.
The unrest began after Moreno ended government subsidies that have helped keep fuel prices low in Ecuador for some 40 years. The move was part of a broader austerity plan related to $4.2 billion from the International Monetary Fund to prop up Ecuador’s government and economy.
The IMF was recommending a careful and slow change in fuel subsidies which, along with tax reform and other measures, would generate savings that would “allow for an increase in social assistance spending over the course of the program.”
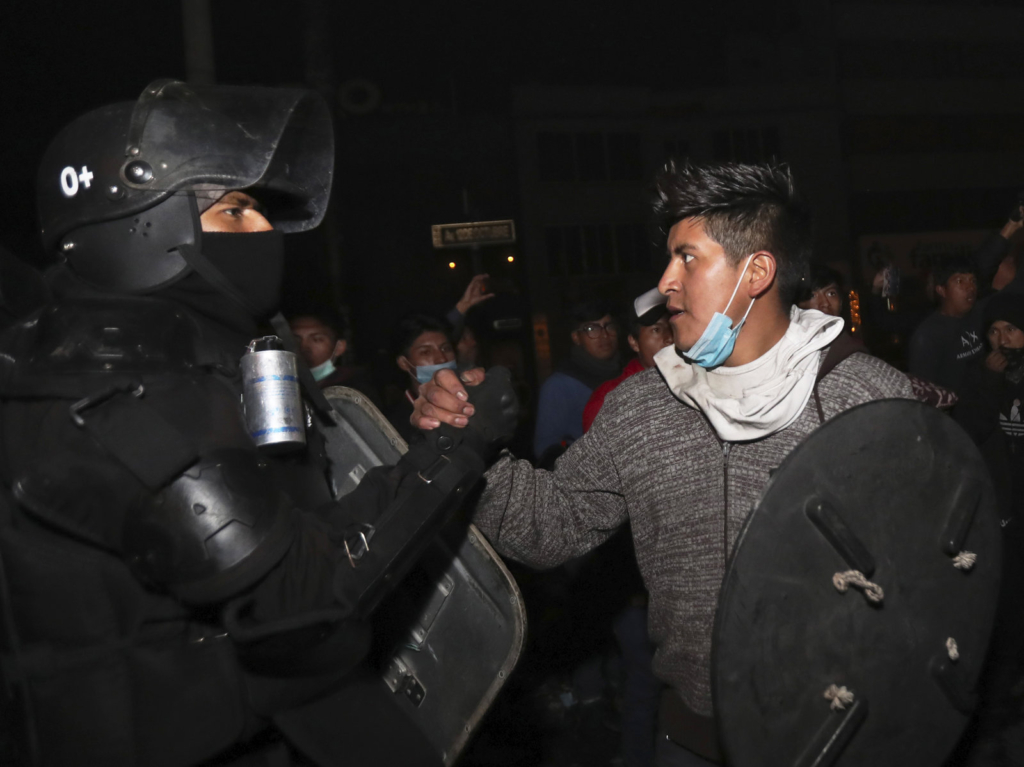

But after Moreno said he was ending the subsidies, the price of diesel fuel more than doubled. Gasoline prices rose as well. Riots broke out, a state of emergency was declared, and thousands of people were arrested or injured. At one point, the chaos drove Moreno and his government to depart the capital city, Quito. […]
The United Nations says that globally, subsidies for fossil fuels are “deeply unsustainable, particularly if we are to seriously curb our CO2 emissions, slow our impact on climate change and reduce air pollution.” That’s because they in effect encourage people to use more fossil fuels or energy derived from fossil fuels.
But the subsidies are popular and politically hard to undo when they keep gas or other energy prices lower than they otherwise would be. Some research has shown that an effective approach can be for governments to move gradually, and replace fuel subsidies with other social spending programs to benefit people who will be hurt financially as fuel subsidies are withdrawn. [more]