With dry taps and toilets, California drought turns desperate – ‘You don’t think of water as privilege until you don’t have it anymore’
By Jennifer Medina
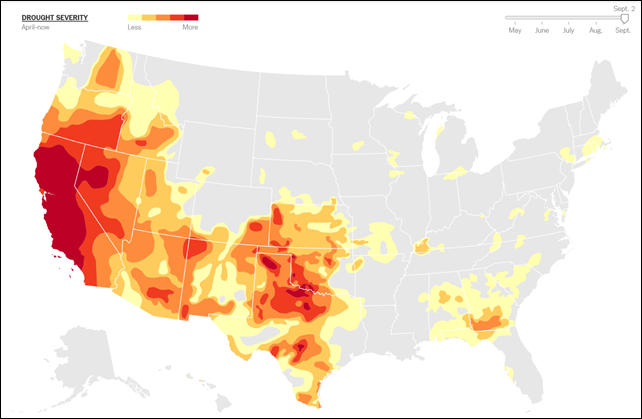
2 October 2014 PORTERVILLE, California (The New York Times) – After a nine-hour day working at a citrus packing plant, her body covered in a sheen of fruit wax and dust, there is nothing Angelica Gallegos wants more than a hot shower, with steam to help clear her throat and lungs. “I can just picture it, that feeling of finally being clean — really refreshed and clean,” Ms. Gallegos, 37, said one recent evening. But she has not had running water for more than five months — nor is there any tap water in her near future — because of a punishing and relentless drought in California. In the Gallegos household and more than 500 others in Tulare County, residents cannot flush a toilet, fill a drinking glass, wash dishes or clothes, or even rinse their hands without reaching for a bottle or bucket. Unlike the Okies who came here fleeing the Dust Bowl of the 1930s, the people now living on this parched land are stuck. “We don’t have the money to move, and who would buy this house without water?” said Ms. Gallegos, who grew up in the area and shares a tidy mobile home with her husband and two daughters. “When you wake up in the middle of the night sick to your stomach, you have to think about where the water bottle is before you can use the toilet.” Now in its third year, the state’s record-breaking drought is being felt in many ways: vanishing lakes and rivers, lost agricultural jobs, fallowed farmland, rising water bills, suburban yards gone brown. But nowhere is the situation as dire as in East Porterville, a small rural community in Tulare County where life’s daily routines have been completely upended by the drying of wells and, in turn, the disappearance of tap water. “Everything has changed,” said Yolanda Serrato, 54, who has spent most of her life here. Until this summer, the lawn in front of her immaculate three-bedroom home was a lush green, with plants dotting the perimeter. As her neighbors’ wells began running dry, Ms. Serrato warned her three children that they should cut down on long showers, but they rebuffed her. “They kept saying, ‘No, no, Mama, you’re just too negative,’ ” she said. Then the sink started to sputter. These days, the family of five relies on a water tank in front of their home that they received through a local charity. The sole neighbor with a working well allows them to hook up to his water at night, saving them from having to use buckets to flush toilets in the middle of the night. On a recent morning, there was still a bit of the neighbor’s well water left, trickling out the kitchen faucet, taking over 10 minutes to fill two three-quart pots. “You don’t think of water as privilege until you don’t have it anymore,” said Ms. Serrato, whose husband works in the nearby fields. “We were very proud of making a life here for ourselves, for raising children here. We never ever expected to live this way.” [more]
With Dry Taps and Toilets, California Drought Turns Desperate
Angelica Gallegos' parents doomed her to a hellish life by giving birth to her. She should kick them both in the crotch.