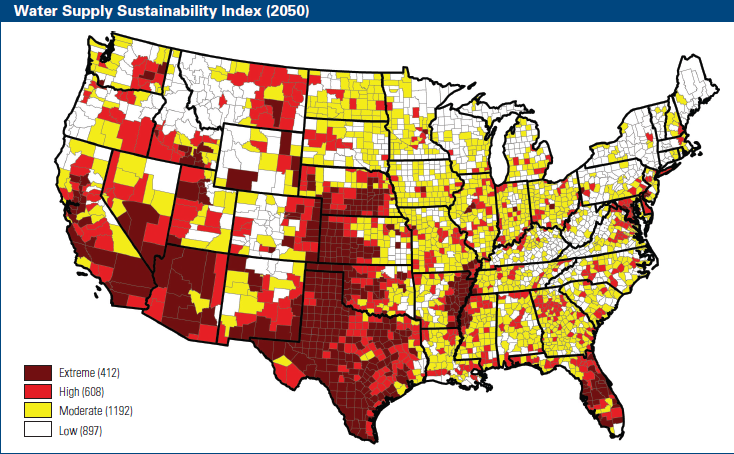
More than one third of US counties face water shortages due to climate change
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Press contact: Eric Young, NRDC, 202-289-2373 or eyoung@nrdc.org WASHINGTON (July 20, 2010) — More than 1,100 U.S. counties — a full one-third of all counties in the lower 48 states — now face higher risks of water shortages by mid-century as the result of global warming, and more than 400 of these counties will be at extremely high risk for water shortages, based on estimates from a new report [pdf] by Tetra Tech for the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC). The report uses publicly available water use data across the United States and climate projections from a set of models used in recent Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) work to evaluate withdrawals related to renewable water supply. The report finds that 14 states face an extreme or high risk to water sustainability, or are likely to see limitations on water availability as demand exceeds supply by 2050. These areas include parts of Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Florida, Idaho, Kansas, Mississippi, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas. In particular, in the Great Plains and Southwest United States, water sustainability is at extreme risk. The more than 400 counties identified as being at greatest risk in the report reflects a 14-times increase from previous estimates. For a look at county- and state-specific maps detailing the report findings (including a Google Earth map), go to http://www.nrdc.org/globalWarming/watersustainability/ and http://rd.tetratech.com/climatechange/projects/nrdc_climate.asp. While detailed modeling of climate change impacts on crop production was beyond the scope of the Tetra Tech analysis, the potential scale of disruption is reflected based on the value of the crops produced in the 1,100 at-risk counties. In 2007, the value of the crops produced in the at-risk counties identified in the report exceeded $105 billion. A separate study compared the Tetra Tech data with county-level crop production data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture; state-specific fact sheets outlining the potential agricultural impacts may be found at http://agcarbonmarkets.com/Science.htm. Dan Lashof, director of the Climate Center at NRDC, said: “This analysis shows climate change will take a serious toll on water supplies throughout the country in the coming decades, with over one out of three U.S. counties facing greater risks of water shortages. Water shortages can strangle economic development and agricultural production and affected communities. As a result, cities and states will bear real and significant costs if Congress fails to take the steps necessary to slow down and reverse the warming trend. Water management and climate change adaptation plans will be essential to lessen the impacts, but they cannot be expected to counter the effects of a warming climate. The only way to truly manage the risks exposed by this report is for Congress to pass meaningful legislation that cuts global warming pollution and allows the U.S. to exercise global leadership on the issue.” …
Report: More than One Out of Three U.S. Counties Face Water Shortages Due to Climate Change