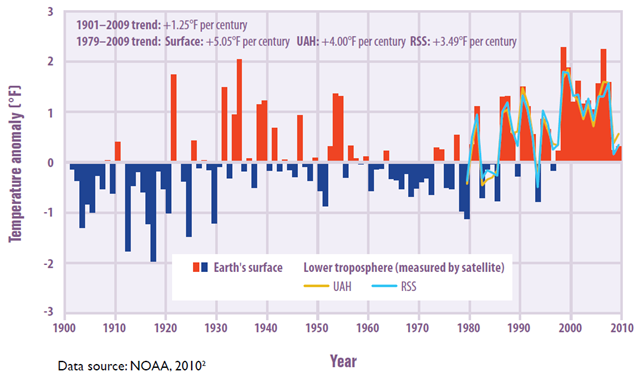
Graph of the Day: Temperatures in the Lower 48 States, 1901–2009
This figure shows how average temperatures in the lower 48 states have changed since 1901. Surface data come from land-based weather stations, while satellite measurements cover the lower troposphere, which is the lowest level of the Earth’s atmosphere (see diagram on p. 20). “UAH” and “RSS” represent two different methods of analyzing the original satellite measurements. This graph uses the 1901 to 2000 average as a baseline for depicting change. Choosing a different baseline period would not change the shape of the trend. Since 1901, temperatures have risen across the lower 48 states at an average rate of 0.13°F per decade (1.3°F per century). Average temperatures have risen more quickly since the late 1970s (0.35 to 0.51°F per decade). Seven of the top 10 warmest years on record for the lower 48 states have occurred since 1990, and the last 10 five-year periods have been the 10 warmest five-year periods on record. Global average surface temperatures have risen at an average rate of 0.13°F per decade since 1901, similar to the rate of warming within the lower 48 states. Since the late 1970s, however, the United States has warmed at nearly twice the global rate. Worldwide, 2000–2009 was the warmest decade on record.