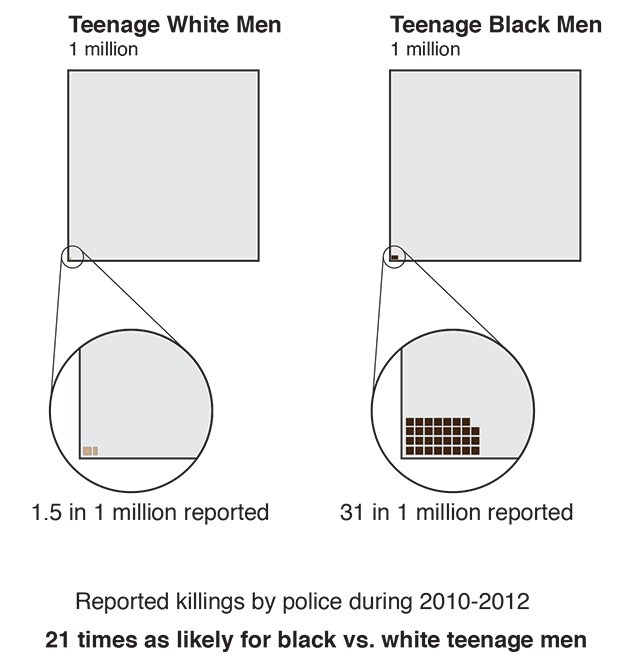
Young African-American men are 21 times more likely to be killed by police than young white men
By Ryan Gabrielson, Ryann Grochowski Jones, and Eric Sagara
10 October 2014 (ProPublica) – Young black males in recent years were at a far greater risk of being shot dead by police than their white counterparts – 21 times greater – according to a ProPublica analysis of federally collected data on fatal police shootings. The 1,217 deadly police shootings from 2010 to 2012 captured in the federal data show that blacks, age 15 to 19, were killed at a rate of 31.17 per million, while just 1.47 per million white males in that age range died at the hands of police. One way of appreciating that stark disparity, ProPublica’s analysis shows, is to calculate how many more whites over those three years would have had to have been killed for them to have been at equal risk. The number is jarring – 185, more than one per week. ProPublica’s risk analysis on young males killed by police certainly seems to support what has been an article of faith in the African American community for decades: Blacks are being killed at disturbing rates when set against the rest of the American population. Our examination involved detailed accounts of more than 12,000 police homicides stretching from 1980 to 2012 contained in the FBI’s Supplementary Homicide Report. The data, annually self-reported by hundreds of police departments across the country, confirms some assumptions, runs counter to others, and adds nuance to a wide range of questions about the use of deadly police force. Colin Loftin, University at Albany professor and co-director of the Violence Research Group, said the FBI data is a minimum count of homicides by police, and that it is impossible to precisely measure what puts people at risk of homicide by police without more and better records. Still, what the data shows about the race of victims and officers, and the circumstances of killings, are “certainly relevant,” Loftin said. “No question, there are all kinds of racial disparities across our criminal justice system,” he said. “This is one example.” The FBI’s data has appeared in news accounts over the years, and surfaced again with the August killing of Michael Brown in Ferguson, Missouri. To a great degree, observers and experts lamented the limited nature of the FBI’s reports. Their shortcomings are inarguable. The data, for instance, is terribly incomplete. Vast numbers of the country’s 17,000 police departments don’t file fatal police shooting reports at all, and many have filed reports for some years but not others. Florida departments haven’t filed reports since 1997 and New York City last reported in 2007. Information contained in the individual reports can also be flawed. Still, lots of the reporting police departments are in larger cities, and at least 1000 police departments filed a report or reports over the 33 years. There is, then, value in what the data can show while accepting, and accounting for, its limitations. Indeed, while the absolute numbers are problematic, a comparison between white and black victims shows important trends. Our analysis included dividing the number of people of each race killed by police by the number of people of that race living in the country at the time, to produce two different rates: the risk of getting killed by police if you are white and if you are black. David Klinger, a University of Missouri-St. Louis professor and expert on police use of deadly force, said racial disparities in the data could result from “measurement error,” meaning that the unreported killings could alter ProPublica’s findings. However, he said the disparity between black and white teenage boys is so wide, “I doubt the measurement error would account for that.” ProPublica spent weeks digging into the many rich categories of information the reports hold: the race of the officers involved; the circumstances cited for the use of deadly force; the age of those killed. [more]