Climate change has worsened global economic inequality – “Most of the poorest countries on Earth are considerably poorer than they would have been without global warming,”
By Josie Garthwaite
22 April 2019
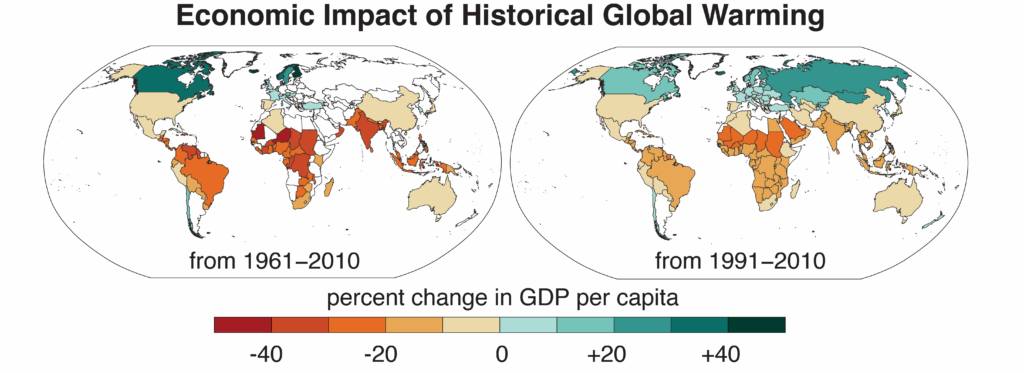
(Stanford University) – A new Stanford University study shows global warming has increased economic inequality since the 1960s. Temperature changes caused by growing concentrations of greenhouse gases in Earth’s atmosphere have enriched cool countries like Norway and Sweden, while dragging down economic growth in warm countries such as India and Nigeria.
“Our results show that most of the poorest countries on Earth are considerably poorer than they would have been without global warming,” said climate scientist Noah Diffenbaugh, lead author of the study published 22 April 2019 in the peer-reviewed Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. “At the same time, the majority of rich countries are richer than they would have been.”
The study, co-authored with Marshall Burke, a Stanford assistant professor of Earth system science, finds that, from 1961 to 2010, global warming decreased the wealth per person in the world’s poorest countries by 17 to 30 percent. Meanwhile, the gap between the group of nations with the highest and lowest economic output per person is now approximately 25 percent larger than it would have been without climate change.
Although economic inequality between countries has decreased in recent decades, the research suggests the gap would have narrowed faster without global warming.
Ideal temperature for economic output
The study builds on previous research in which Burke and co-authors analyzed 50 years of annual temperature and GDP measurements for 165 countries to estimate the effects of temperature fluctuations on economic growth. They demonstrated that growth during warmer than average years has accelerated in cool nations and slowed in warm nations.
“The historical data clearly show that crops are more productive, people are healthier and we are more productive at work when temperatures are neither too hot nor too cold,” Burke explained. “This means that in cold countries, a little bit of warming can help. The opposite is true in places that are already hot.”
In the current study, Diffenbaugh and Burke combined Burke’s previously published estimates with data from more than 20 climate models developed by research centers around the world. Using the climate models to isolate how much each country has already warmed due to human-caused climate change, the researchers were able to determine what each country’s economic output might have been had temperatures not warmed.
To account for uncertainty, the researchers calculated more than 20,000 versions of what each country’s annual economic growth rate could have been without global warming. The estimates in the paper capture the range of outcomes delivered by those thousands of different routes.
“For most countries, whether global warming has helped or hurt economic growth is pretty certain,” said Burke. Tropical countries, in particular, tend to have temperatures far outside the ideal for economic growth. “There’s essentially no uncertainty that they’ve been harmed.”
It’s less clear how warming has influenced growth in countries in the middle latitudes, including the United States, China and Japan. For these and other temperate-climate nations, the analysis reveals economic impacts of less than 10 percent.
“A few of the largest economies are near the perfect temperature for economic output. Global warming hasn’t pushed them off the top of the hill, and in many cases, it has pushed them toward it,” Burke said. “But a large amount of warming in the future will push them further and further from the temperature optimum.”
Dragged down by warming
While the impacts of temperature may seem small from year to year, they can yield dramatic gains or losses over time. “This is like a savings account, where small differences in the interest rate will generate large differences in the account balance over 30 or 50 years,” said Diffenbaugh, the Kara J. Foundation professor in Stanford’s School of Earth, Energy & Environmental Sciences (Stanford Earth). For example, after accumulating decades of small effects from warming, India’s economy is now 31 percent smaller than it would have been in the absence of global warming.
At a time when climate policy negotiations often stall over questions of how to equitably divide responsibility for curbing future warming, Diffenbaugh and Burke’s analysis offers a new measure of the price many countries have already paid. “Our study makes the first accounting of exactly how much each country has been impacted economically by global warming, relative to its historical greenhouse gas contributions,” said Diffenbaugh, who is also Kimmelman Family senior fellow in the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment.
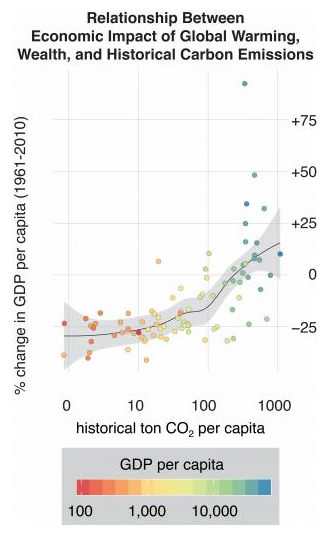
While the biggest emitters enjoy on average about 10 percent higher per capita GDP today than they would have in a world without warming, the lowest emitters have been dragged down by about 25 percent. “This is on par with the decline in economic output seen in the U.S. during the Great Depression,” Burke said. “It’s a huge loss compared to where these countries would have been otherwise.”
The researchers emphasize the importance of increasing sustainable energy access for economic development in poorer countries. “The more these countries warm up, the more drag there’s going to be on their development,” Diffenbaugh said. “Historically, rapid economic development has been powered by fossil fuels. Our finding that global warming has exacerbated economic inequality suggests that there is an added economic benefit of energy sources that don’t contribute to further warming.”
Climate change has worsened global economic inequality
ABSTRACT: Understanding the causes of economic inequality is critical for achieving equitable economic development. To investigate whether global warming has affected the recent evolution of inequality, we combine counterfactual historical temperature trajectories from a suite of global climate models with extensively replicated empirical evidence of the relationship between historical temperature fluctuations and economic growth. Together, these allow us to generate probabilistic country-level estimates of the influence of anthropogenic climate forcing on historical economic output. We find very high likelihood that anthropogenic climate forcing has increased economic inequality between countries. For example, per capita gross domestic product (GDP) has been reduced 17–31% at the poorest four deciles of the population-weighted country-level per capita GDP distribution, yielding a ratio between the top and bottom deciles that is 25% larger than in a world without global warming. As a result, although between-country inequality has decreased over the past half century, there is ∼90% likelihood that global warming has slowed that decrease. The primary driver is the parabolic relationship between temperature and economic growth, with warming increasing growth in cool countries and decreasing growth in warm countries. Although there is uncertainty in whether historical warming has benefited some temperate, rich countries, for most poor countries there is >90% likelihood that per capita GDP is lower today than if global warming had not occurred. Thus, our results show that, in addition to not sharing equally in the direct benefits of fossil fuel use, many poor countries have been significantly harmed by the warming arising from wealthy countries’ energy consumption.
SIGNIFICANCE: We find that global warming has very likely exacerbated global economic inequality, including ∼25% increase in population-weighted between-country inequality over the past half century. This increase results from the impact of warming on annual economic growth, which over the course of decades has accumulated robust and substantial declines in economic output in hotter, poorer countries—and increases in many cooler, wealthier countries—relative to a world without anthropogenic warming. Thus, the global warming caused by fossil fuel use has likely exacerbated the economic inequality associated with historical disparities in energy consumption. Our results suggest that low-carbon energy sources have the potential to provide a substantial secondary development benefit, in addition to the primary benefits of increased energy access.


