Ocean heatwaves threaten survival of dolphins – “The reproductive success of females appears to have not returned to normal levels, even after six years”
1 April 2019 (UZH) – An unprecedented marine heatwave had long-lasting negative impacts on both survival and birth rates on the iconic dolphin population in Shark Bay, Western Australia. Researchers at UZH have now documented that climate change may have more far-reaching consequences for the conservation of marine mammals than previously thought.
Shark Bay in Western Australia in early 2011: A heatwave causes the water temperatures to rise to more than four degrees above the annual average. The extended period caused a substantial loss of seagrass, which drives the Shark Bay ecosystem, in this coastal area, a UNESCO world heritage site.
Researchers from UZH have now investigated how this environmental damage has affected survival and reproduction of dolphins. They used long-term data on hundreds of animals collected over a ten-year period from 2007 to 2017. Their analyses revealed that the dolphins’ survival rate had fallen by 12 percent following the heatwave of 2011. Moreover, female dolphins were giving birth to fewer calves – a phenomenon that lasted at least until 2017.
Negative influence of the heatwave is unprecedented
“The extent of the negative influence of the heatwave surprised us,” says Sonja Wild, former PhD candidate at the University of Leeds and first author of the study. “It is particularly unusual that the reproductive success of females appears to have not returned to normal levels, even after six years.” There are several possible explanations for this phenomenon, for instance neglect of calves, increased newborn mortality, delayed sexual maturity or a combination thereof, but researchers have not yet been able to investigate them in detail.
Tool-using dolphins are less affected
Interestingly, the heatwave did not have the same effect on all dolphin groups. Dolphins that use sponges as tools – a socially learned foraging technique that helps dolphins to locate food in deep water – were not as badly affected as those that do not use this technique. “Nevertheless, our work raises concerns that such sudden events might have quite negative long-term effects even in groups of marine mammals that are known to adapt usually well to novel environmental conditions,” says Sonja Wild.
Dire news for entire oceanic ecosystems?
The UZH researchers show in their study for the first time that marine heatwaves not only affect organisms at lower levels of the food chain, but also might have considerable long-term consequences for the animals at the top, such as dolphins. “Marine heatwaves are likely to occur more frequently in the future due to climate change,” says study leader Michael Krützen, professor at the Department of Anthropology at UZH. “This is worrying not only for the long-term prospects of marine mammal populations, but also for the entire oceanic ecosystems.”
The study was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation, the National Geographic Society, the SeaWorld Research and Rescue Foundation, the W.V. Scott Foundation and the A.H. Schultz Foundation.
Contact
- Prof. Michael Krützen, Department of Anthropology and Museum of Anthropology, University of Zurich, Phone +41 44 635 54 12, michael.kruetzen@aim.uzh.ch
- Sonja Wild, Department of Anthropology and Museum of Anthropology, University of Zurich, Phone +44 792 6171 262, sonja.wild@uzh.ch
Climate Change Threat to Dolphins’ Survival
Long-term decline in survival and reproduction of dolphins following a marine heatwave
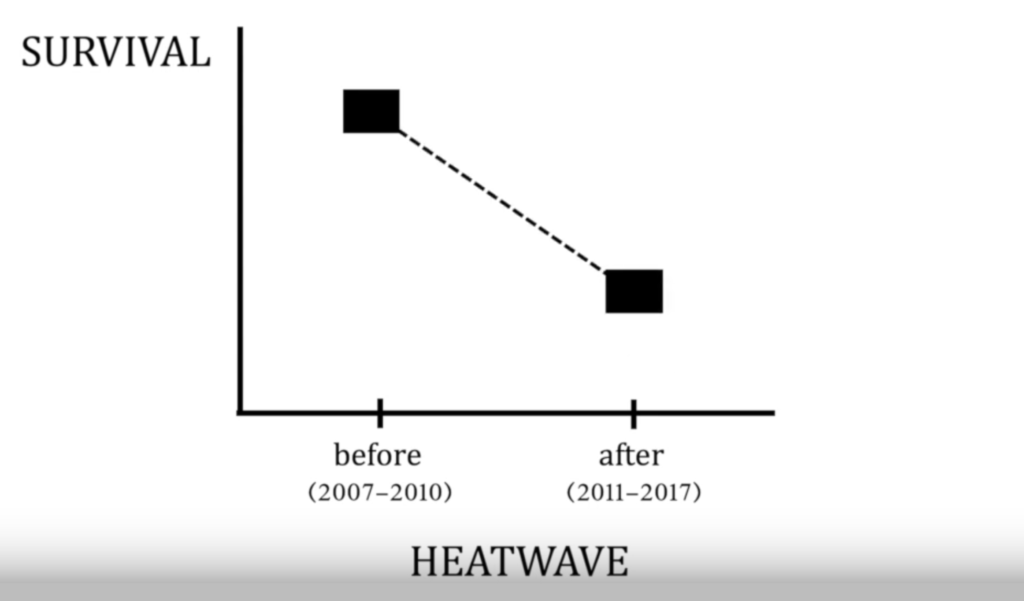
ABSTRACT: One of many challenges in the conservation of biodiversity is the recent trend in the frequency and intensity of extreme climatic events [1]. The Shark Bay World Heritage Area, Western Australia, endured an unprecedented marine heatwave in 2011. Catastrophic losses of habitat-forming seagrass meadows followed [2], along with mass mortalities of invertebrate and fish communities [3]. Our long-term demographic data on Shark Bay’s resident Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops aduncus) population revealed a significant decline in female reproductive rates following the heatwave. Moreover, capture–recapture analyses indicated 5.9% and 12.2% post-heatwave declines in the survival of dolphins that use tools to forage and those that do not, respectively. This implies that the tool-using dolphins may have been somewhat buffered against the cascading effects of habitat loss following the heatwave by having access to a less severely affected foraging niche [4]. Overall, however, lower survival has persisted post-heatwave, suggesting that habitat loss following extreme weather events may have prolonged, negative impacts on even behaviourally flexible, higher-trophic level predators.
Long-term decline in survival and reproduction of dolphins following a marine heatwave