Plastic pollution found in every tiny animal tested in the Mariana Trench, the lowest point in any ocean – “What you put in the trench stays in the trench”
By Ed Yong
27 February 2019
(The Atlantic) – Alan Jamieson remembers seeing it for the first time: a small, black fiber floating in a tube of liquid. It resembled a hair, but when Jamieson examined it under a microscope, he realized that the fiber was clearly synthetic—a piece of plastic. And worryingly, his student Lauren Brooks had pulled it from the gut of a small crustacean living in one of the deepest parts of the ocean.
For the past decade, Jamieson, a marine biologist at Newcastle University, has been sending vehicles to the bottom of marine trenches, which can be as deep as the Himalayas are tall. Once there, these landers have collected amphipods—scavenger relatives of crabs and shrimp that thrive in the abyss. Jamieson originally wanted to know how these animals differ from one distant trench to another. But a few years ago, almost on a whim, he decided to analyze their body for toxic, human-made pollutants such as polychlorinated biphenyls, or PCBs, which have been banned for decades but which persist in nature for much longer.
The team found PCBs galore. Some amphipods were carrying levels 50 times higher than those seen in crabs from one of China’s most polluted rivers. When the news broke, Jamieson was inundated with calls from journalists and concerned citizens. And in every discussion, one question kept coming up: What about plastics?
The world produces an estimated 10 tons of plastic a second, and between 5 million and 14 million tons sweep into the oceans every year. Some of that debris washes up on beaches, even on the world’s most isolated islands. About 5 trillion pieces currently float in surface waters, mostly in the form of tiny, easy-to-swallow fragments that have ended up in the gut of albatrosses, sea turtles, plankton, fish, and whales. But those pieces also sink, snowing into the deep sea and upon the amphipods that live there.
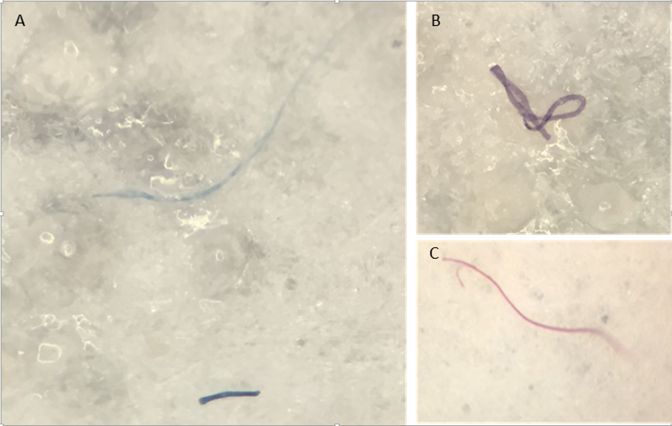
Brooks eventually found plastic fibers and fragments in 72 percent of the amphipods that the team collected, from all six trenches that they had surveyed. In the least polluted of these sites, half of the amphipods had swallowed at least one piece of plastic. In the 6.8-mile-deep Mariana Trench, the lowest point in any ocean, all of the specimens had plastic in their gut. […]
Food is scarce in the deep, so amphipods can’t afford to be fussy. They’ll eat pretty much anything, which makes them particularly vulnerable to plastics. And since they sit at the bottom of the trench food webs, their catholic appetite can doom entire ecosystems. “They’re like bags of peanuts,” Jamieson says. “Everything else eats amphipods—shrimp, fish—and they’ll end up consuming plastics, too. And when the fish die, they get consumed by amphipods, and it goes round and round in circles.”
“What you put in the trench stays in the trench,” he adds. Which means that the plastic problem “is only going to get worse. Anything going in there isn’t coming back.” [more]