Annual survey: ‘Beekeepers say losses remain higher than the level that they consider to be sustainable’
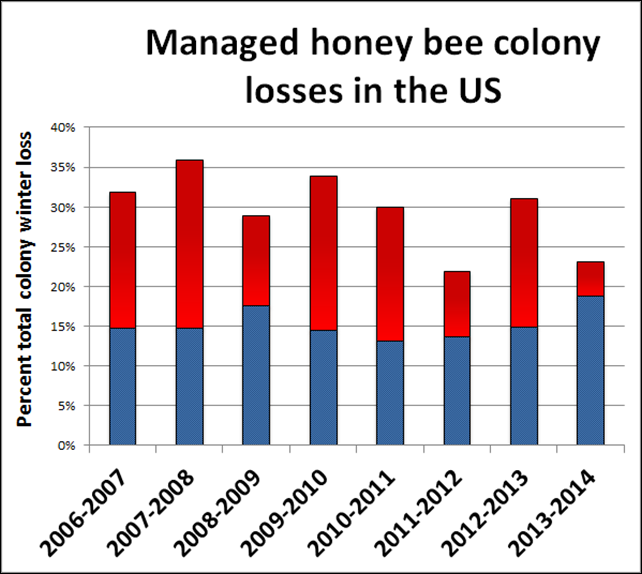
USDA Announces Fall Summit on Bee Nutrition and Forage; Launches “Bee Watch” Website to Broadcast Bee Activity and Increase Public Awareness of the Role of Pollinators in Crop Production WASHINGTON, May 15, 2014 – A yearly survey of beekeepers, released today, shows fewer colony losses occurred in the United States over the winter of 2013-2014 than in recent years, but beekeepers say losses remain higher than the level that they consider to be sustainable. According to survey results, total losses of managed honey bee colonies from all causes were 23.2 percent nationwide. That number is above the 18.9 percent level of loss that beekeepers say is acceptable for their economic sustainability, but is a marked improvement over the 30.5 percent loss reported for the winter of 2012-2013, and over the eight-year average loss of 29.6 percent. More than three-fourths of the world’s flowering plants rely on pollinators, such as bees, to reproduce, meaning pollinators help produce one out of every three bites of food Americans eat. “Pollinators, such as bees, birds and other insects are essential partners for farmers and ranchers and help produce much of our food supply. Healthy pollinator populations are critical to the continued economic well-being of agricultural producers,” said Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack. “While we’re glad to see improvement this year, losses are still too high and there is still much more work to be done to stabilize bee populations.” There is no way to tell why the bees did better this year, according to both Pettis and Dennis vanEngelsdorp, a University of Maryland assistant professor who is the leader of the survey and director of the Bee Informed Partnership. Although the survey, conducted by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the University of Maryland Bee Informed Partnership shows improvement, losses remain above the level that beekeepers consider to be economically sustainable. This year, almost two-thirds of the beekeepers responding reported losses greater than the 18.9 percent threshold. “Yearly fluctuations in the rate of losses like these only demonstrate how complicated the whole issue of honey bee heath has become, with factors such as viruses and other pathogens, parasites like varroa mites, problems of nutrition from lack of diversity in pollen sources, and even sublethal effects of pesticides combining to weaken and kill bee colonies,” said Jeff Pettis, co-author of the survey and research leader of the Agricultural Research Service (ARS) Bee Research Laboratory in Beltsville, Maryland. ARS is USDA’s chief intramural scientific research agency. The winter losses survey covers the period from October 2013 through April 2014. About 7,200 beekeepers responded to the voluntary survey. A complete analysis of the bee survey data will be published later this year. The summary of the analysis is at Colony Loss 2013-2014. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) also announced today that it will hold a summit this fall aimed at addressing the nutrition and forage needs of pollinators. The summit will take place in Washington D.C. on October 20-21 and will be attended by a consortium of public, private, and non-governmental organizations. Attendees will discuss the most recent research related to pollinator loss and work to identify solutions. Additionally, today USDA launched the People’s Garden Apiary bee cam at the USDA headquarters in Washington, D.C. as an additional effort to increase public awareness about the reduction of bee populations and to inform Americans about actions they can take to support the recovery of pollinator populations. The USDA “Bee Watch” website ( www.usda.gov/beewatch) will broadcast honey bee hive activity live over the Internet 24 hours per day, 7 days per week. Created in 2010, the People’s Garden Apiary is home to two beehives. The bees are Italian queens, the most common bee stock and the same used in many honey bee colonies throughout the United States. In March of 2014, Secretary Vilsack created a Pollinator Working Group, under the leadership of Deputy Secretary Krysta Harden, to better coordinate efforts, leverage resources, and increase focus on pollinator issues across USDA agencies. USDA personnel from ten Department agencies (Agricultural Research Service, National Institute of Food and Agriculture, Farm Services Agency, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, Economic Research Service, Forest Service, Agricultural Marketing Service, Risk Management Agency and Rural Development) meet regularly to coordinate and evaluate efforts as USDA strives toward improving pollinator health and ensuring our pollinators continuing contributions to our nation’s environment and food security. Earlier this year, USDA made $3 million available to help agriculture producers in five states (North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Michigan) provide floral forage habitats to benefit pollinating species on working lands. The Honey Bee Pollinator Effort is intended to encourage farmers and ranchers to grow alfalfa, clover and other flowering habitat for bees and other pollinators. The President’s fiscal year 2015 budget proposal provides $71 million for pollinator health activities through multiple USDA agencies. This includes an increase of $40 million in combined mandatory and discretionary funds to advance efforts, in consultation with the Environmental Protection Agency and other Federal partners, to respond to the decline in honey bee health and ensure their recovery. This coordinated effort is focused on targeted research that addresses multifactorial stressors, their interaction, and identification and implementation of measures to improve and increase habitat available to pollinators on Federal and private lands. In addition, this initiative will help prevent introductions of invasive bees, bee diseases, and parasites; document the status of honey bee health factors associated with bee losses and honey bee production; and work with stakeholders on best management practices. A coordinated communication strategy, including outreach and education, will engage the public to help solve this important challenge.
Yearly Survey Shows Better Results for Pollinators, but Losses Remain Significant
May 6, 2014 Dennis vanEngelsdorp1*, Nathalie Steinhauer1, Karen Rennich1, Michael Wilson2, Kathy Baylis3, Dewey M. Caron4, Keith S. Delaplane5, Jamie Ellis6, Kathleen Lee7, Eugene J. Lengerich8, Jeff Pettis9, Robyn Rose10, Ramesh Sagili4, John Skinner2, Angela M. Spleen8, David R. Tarpy11, Dominic Travis7, James T. Wilkes12 for the Bee Informed Partnership. Note: This is a preliminary analysis. A more detailed final report is being prepared for publication at a later date. The Bee Informed Partnership (http://beeinformed.org), in collaboration with the Apiary Inspectors of America (AIA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), is releasing preliminary results for the eighth annual national survey of honey bee colony losses. For the 2013/2014 winter season, 7,183 beekeepers in the United States (U.S.) responded. Collectively, they managed 564,522 colonies in October 2013, 21.7% of the country’s 2.6 million colonies. For the winter of 2013/14, 23.2% of managed honey bee colonies in the U.S. died. Nearly two-thirds of the respondents (65.4%) experienced winter colony loss rates greater than the average self-reported acceptable winter mortality rate of 18.9%. The 2013/14 winter colony loss rate of 23.2% is 7.3 points (or 23.9%) lower than the previous years’ (2012/13) estimate of 30.5% loss. (Figure 1) and is notably lower than the 8-year average total loss of 29.6% . Preliminary results for the 2013/14 survey indicate that 20.0% of all colonies managed between April 1 2013 and Oct 1 2013 died. Responding beekeepers who managed bees over the entire April 2013 – April 2014 survey period reported losing 34.2% of the 670,568 colonies managed over this period. The annual loss differs from the sum of summer and winter losses reported above because the respondent pool differed as only respondents who reported for both the summer and winter period are included in the annual loss rate calculation. The 2012/13 survey expanded beyond only winter mortality estimates to improve our understanding of colony losses by also reporting on summer and annual colony mortality rates. Results from the 2012/13 survey indicated that that summer colony losses (between April 1 2012 and Oct 1 2012) were 25.3%. Loss estimate for the 12-month period (between April 1, 2012 and March 30, 2013) was 45.2%. This survey was conducted by the Bee Informed Partnership, which receives a majority of its funding from the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, USDA (award number: 2011-67007-20017). 1. University of Maryland, dennis.vanengelsdorp@gmail.com, 717-884-2147
2. University of Tennessee
3. University of Illinois
4. Oregon State University
5. University of Georgia
6. University of Florida
7. University of Minnesota
8. The Pennsylvania State University – Hershey
9. USDA-ARS Bee Research Lab
10. USDA Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service
11. North Carolina State University
12. Appalachian State University *Corresponding author 1. Based on NASS Honey report 2013 figures 2. Previous survey results found a total colony loss in the winters of 30.5% in the winter of 2012/2013, 21.9% in 2011/2012, 30% in 2010/2011, 34% in 2009/2010, 29% in 2008/2009, 36% in 2007/2008, and 32% in 2006/2007 (see figure attached)
Preliminary Results: Honey Bee Colony Losses in the United States, 2013-2014