U.S. sees array of new threats at Japan’s nuclear plant – ‘One missed step could make the situation much, much worse’
By JAMES GLANZ and WILLIAM J. BROAD
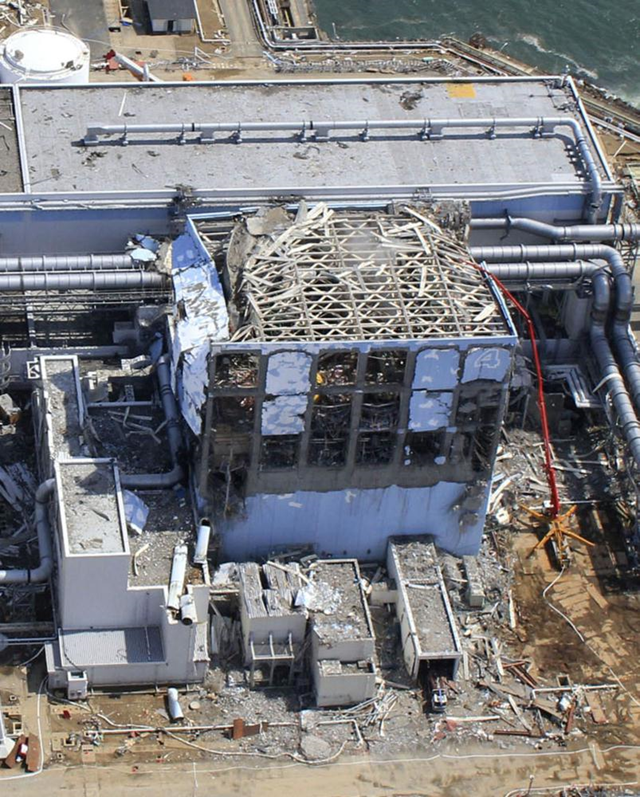
5 April 2011 United States government engineers sent to help with the crisis in Japan are warning that the troubled nuclear plant there is facing a wide array of fresh threats that could persist indefinitely, and that in some cases are expected to increase as a result of the very measures being taken to keep the plant stable, according to a confidential assessment prepared by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Among the new threats that were cited in the assessment, dated March 26, are the mounting stresses placed on the containment structures as they fill with radioactive cooling water, making them more vulnerable to rupture in one of the aftershocks rattling the site after the earthquake and tsunami of March 11. The document also cites the possibility of explosions inside the containment structures due to the release of hydrogen and oxygen from seawater pumped into the reactors, and offers new details on how semimolten fuel rods and salt buildup are impeding the flow of fresh water meant to cool the nuclear cores. In recent days, workers have grappled with several side effects of the emergency measures taken to keep nuclear fuel at the plant from overheating, including leaks of radioactive water at the site and radiation burns to workers who step into the water. The assessment, as well as interviews with officials familiar with it, points to a new panoply of complex challenges that water creates for the safety of workers and the recovery and long-term stability of the reactors. While the assessment does not speculate on the likelihood of new explosions or damage from an aftershock, either could lead to a breach of the containment structures in one or more of the crippled reactors, the last barriers that prevent a much more serious release of radiation from the nuclear core. If the fuel continues to heat and melt because of ineffective cooling, some nuclear experts say, that could also leave a radioactive mass that could stay molten for an extended period. The document, which was obtained by The New York Times, provides a more detailed technical assessment than Japanese officials have provided of the conundrum facing the Japanese as they struggle to prevent more fuel melting at the Fukushima Daiichi plant. But it appears to rely largely on data shared with American experts by the Japanese. Among other problems, the document raises new questions about whether pouring water on nuclear fuel in the absence of functioning cooling systems can be sustained indefinitely. Experts have said the Japanese need to continue to keep the fuel cool for many months until the plant can be stabilized, but there is growing awareness that the risks of pumping water on the fuel present a whole new category of challenges that the nuclear industry is only beginning to comprehend. …